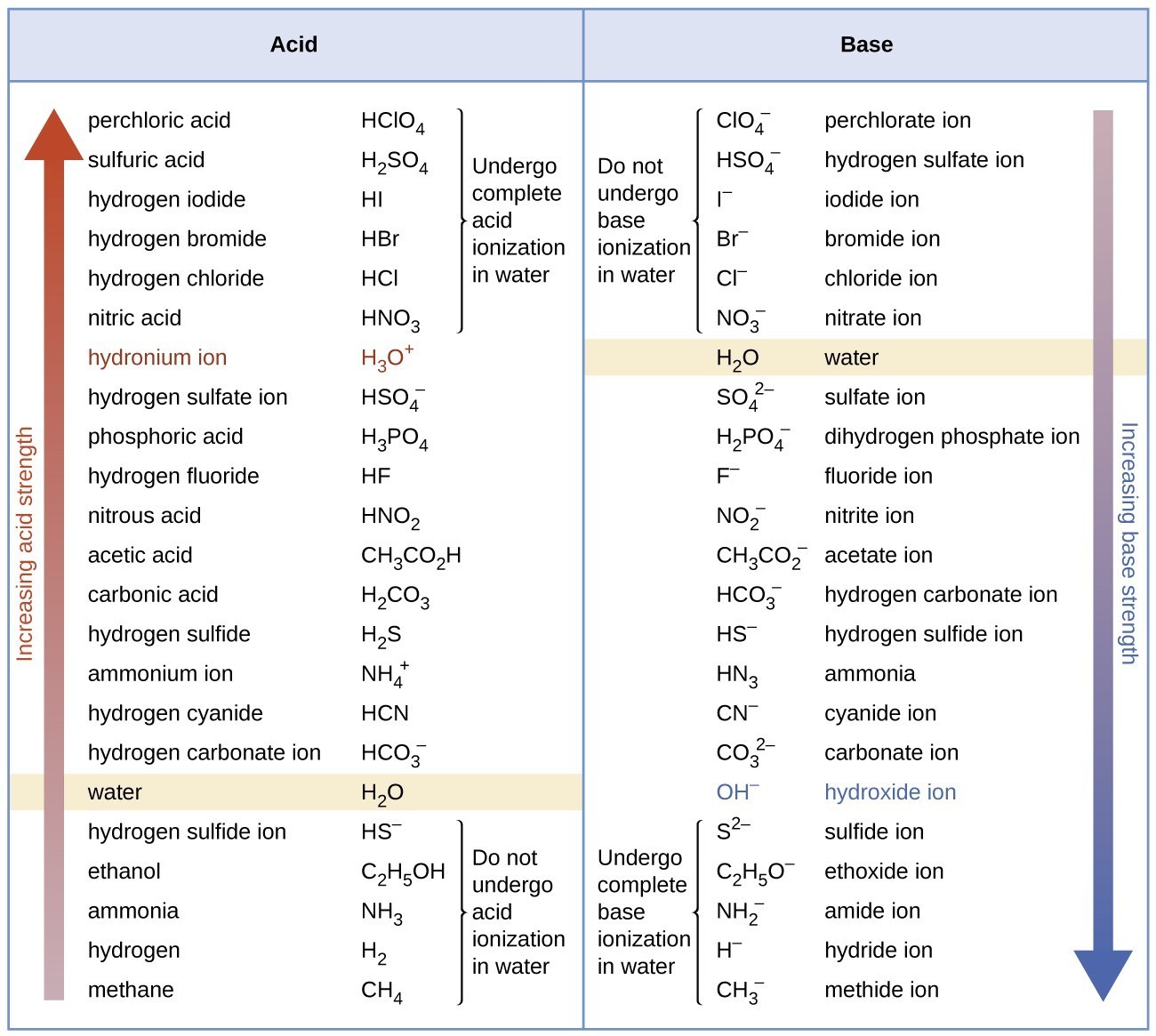
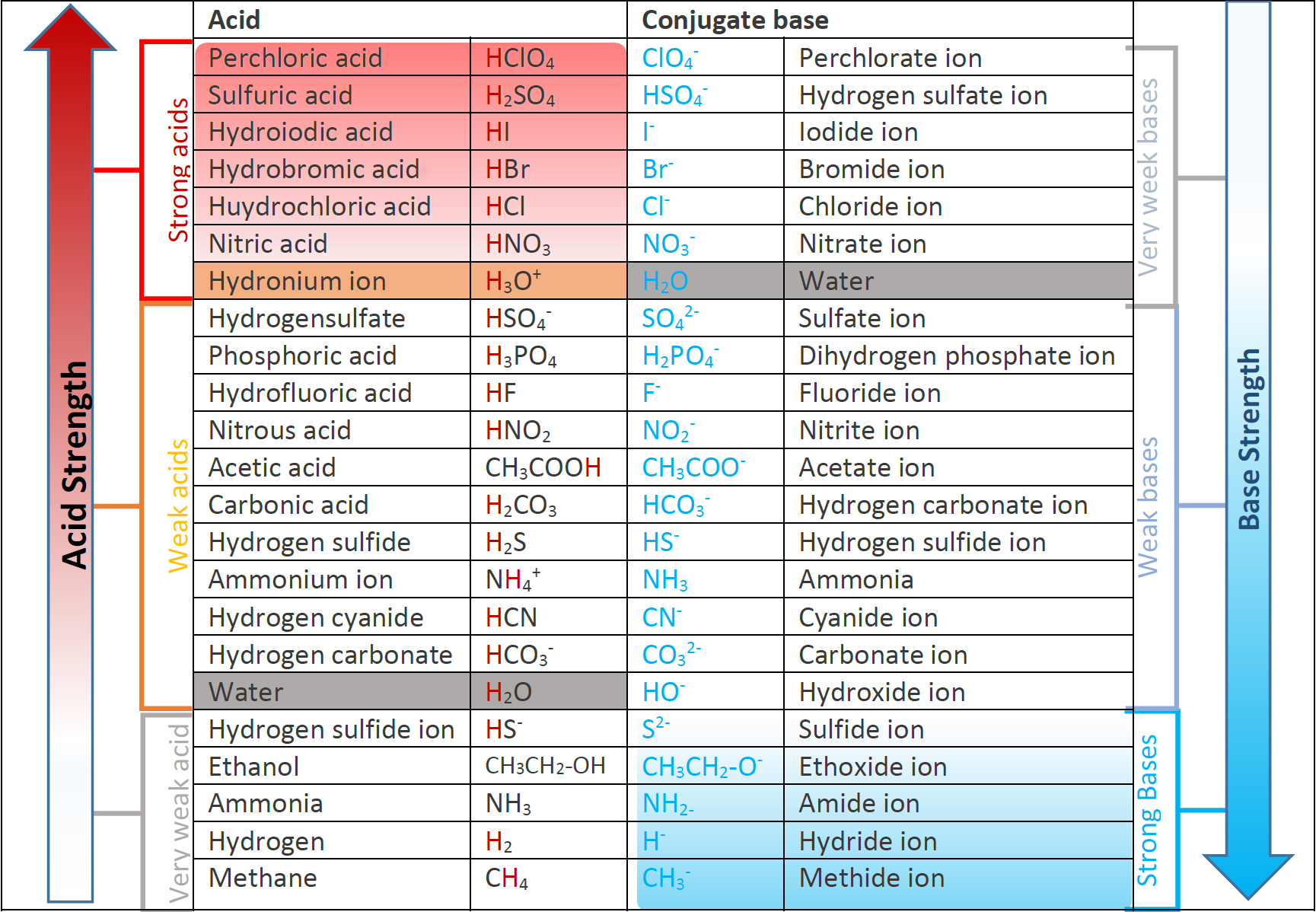
Web figure 14.3.3 lists a series of acids and bases in order of the decreasing strengths of the acids and the corresponding increasing strengths of the bases. A weak acid does not completely ionize in water, yielding only small amounts of \(\ce{h3o+}\) and \(\ce{a^{−}}\). A stronger acid (larger ka) has a smaller p ka, and a. Web definitions of ph, poh, and the ph scale. For each acid, the ionization reaction shows the acid’s conjugate base.
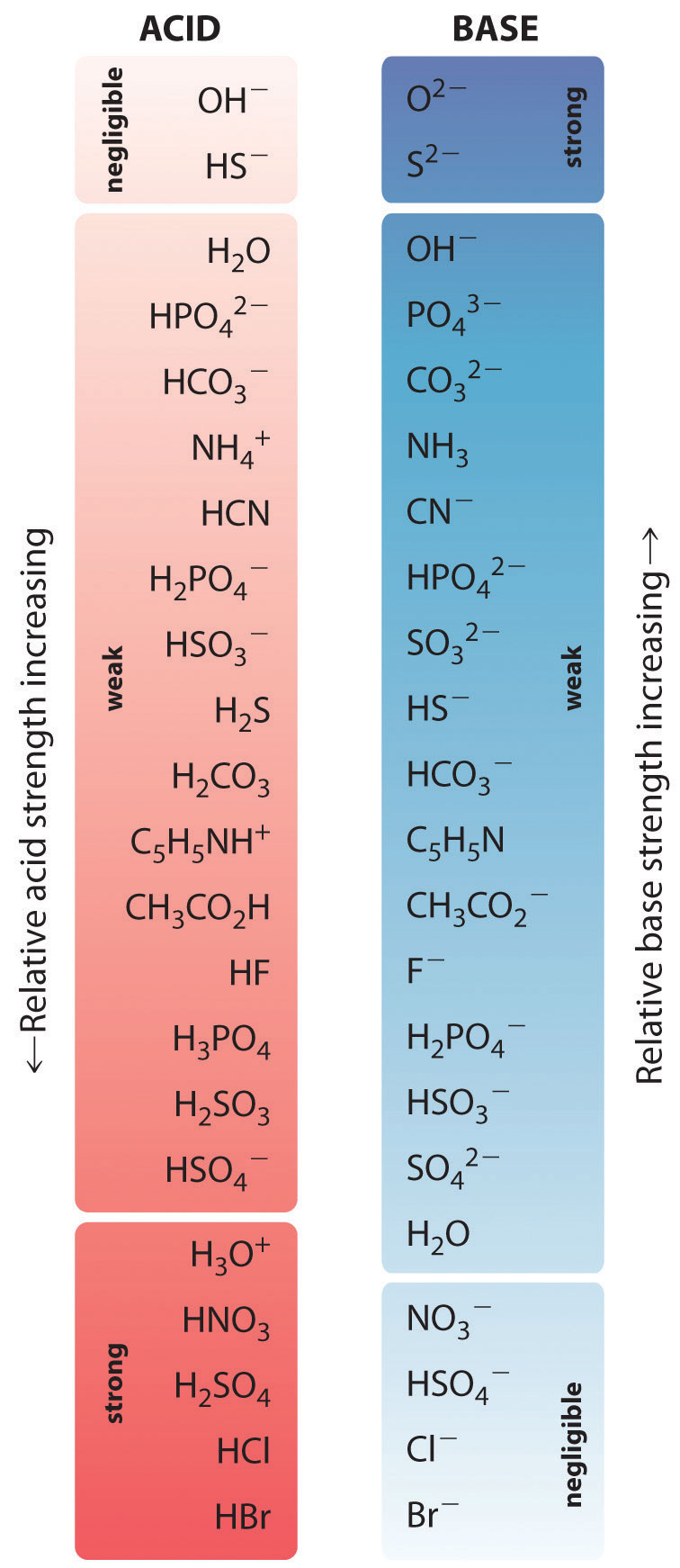
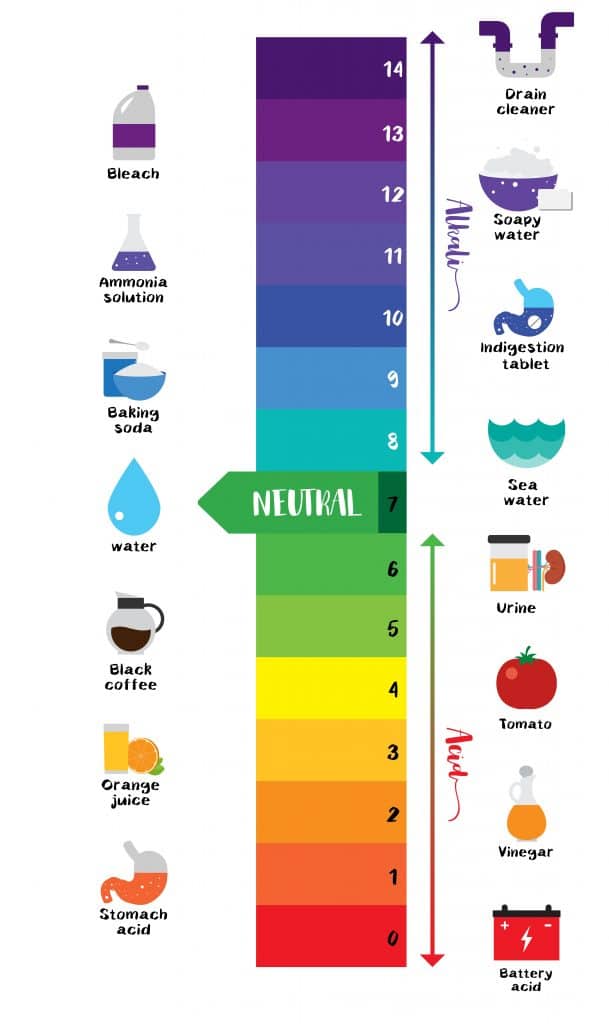
Web acid strength is the tendency of an acid, symbolised by the chemical formula, to dissociate into a proton, +, and an anion,. The terms strong and weak describe the ability of acid and base solutions to conduct electricity. Web a strong acid yields 100% (or very nearly so) of \(\ce{h3o+}\) and \(\ce{a^{−}}\) when the acid ionizes in water. Web the relative strength of an acid or base is the extent to which it ionizes when dissolved in water. Web use this acids and bases chart to find the relative strength of the most common acids and bases.
A guide to acids, acid strength, and concentration. Web a reactivity series, or acid strength chart, provides a visual representation of the relative strength of various acids. Examples of strong acids are hydrochloric acid. Web use this acids and bases chart to find the relative strength of the most common acids and bases. A stronger acid (larger ka) has a smaller p ka, and a.
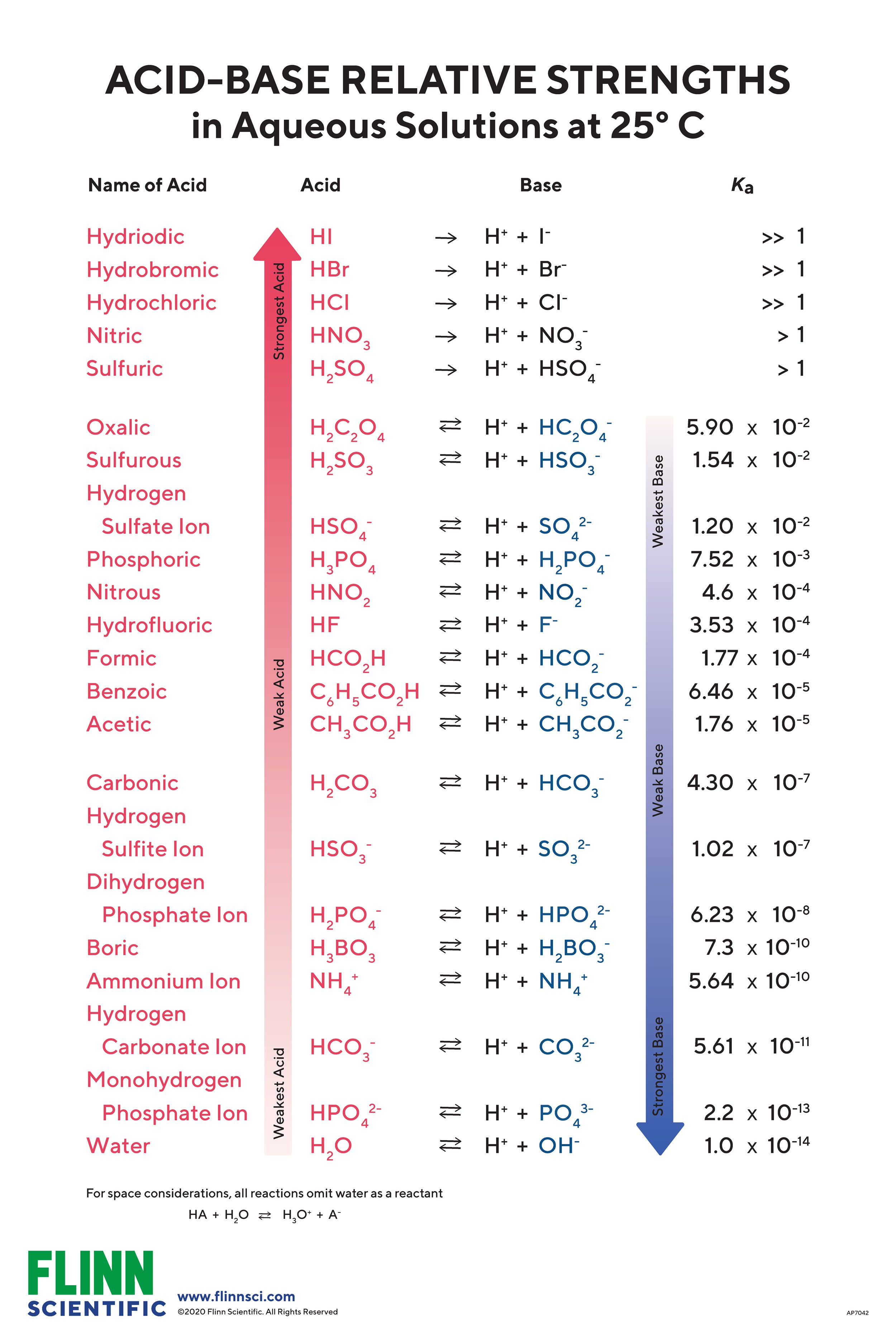
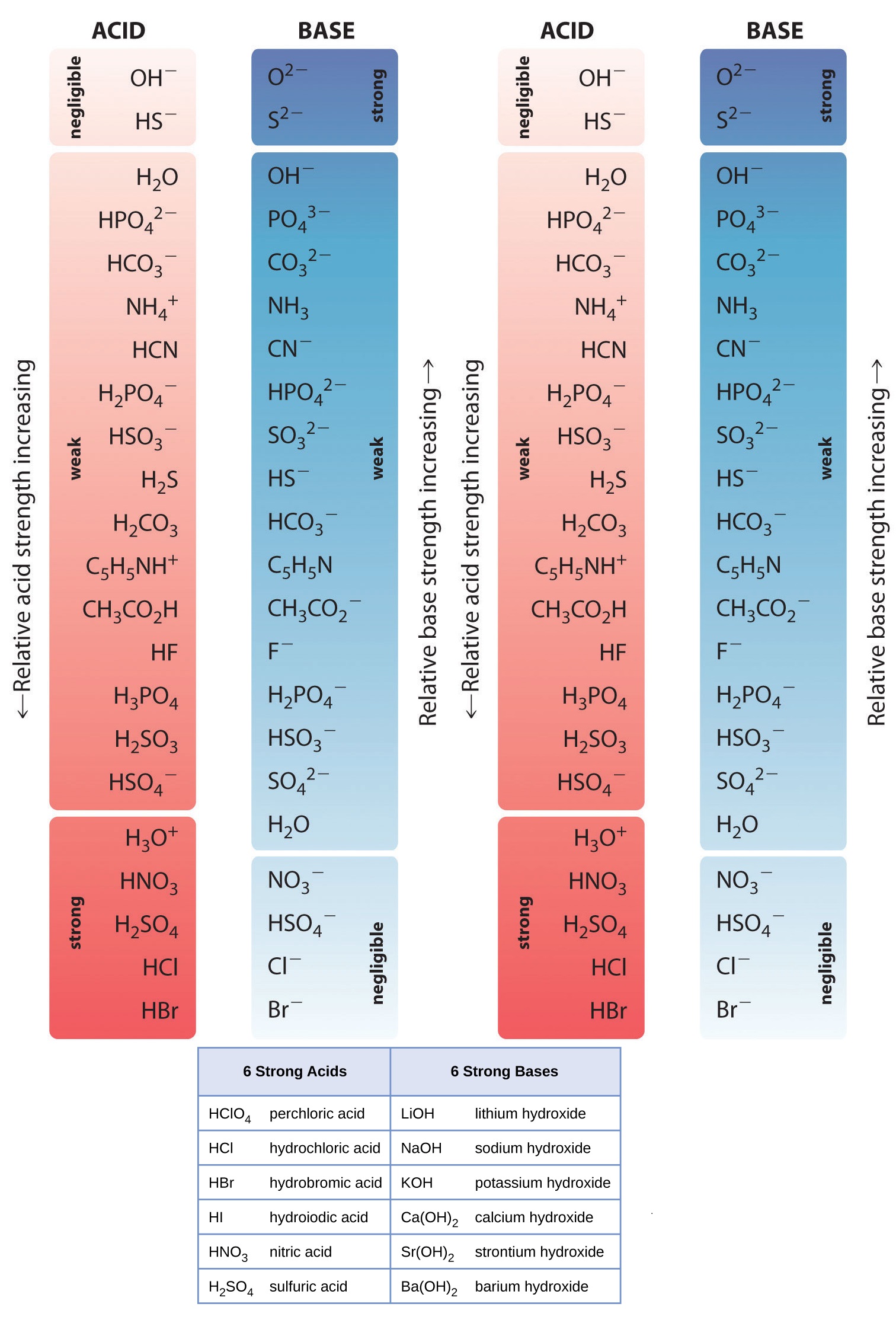
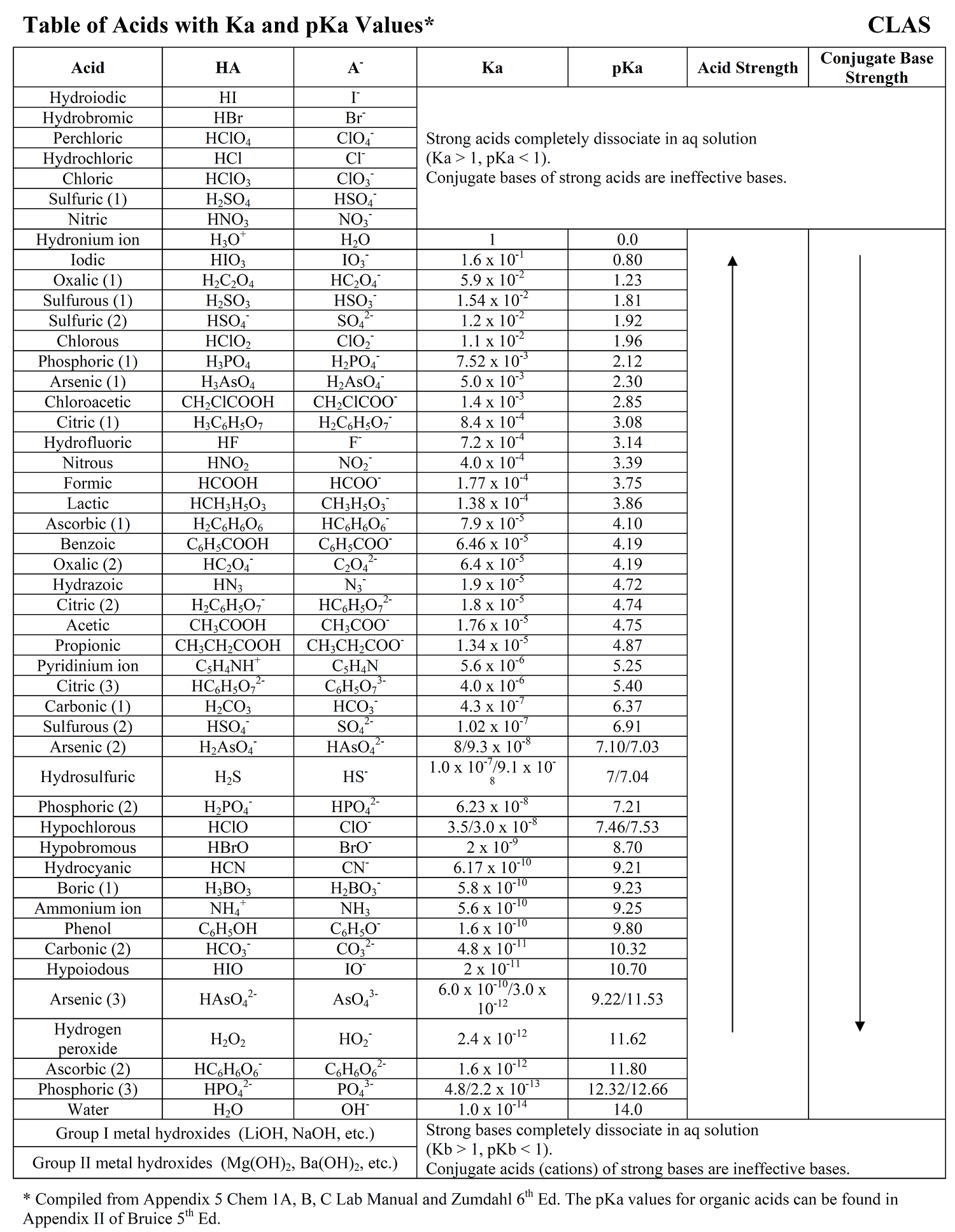
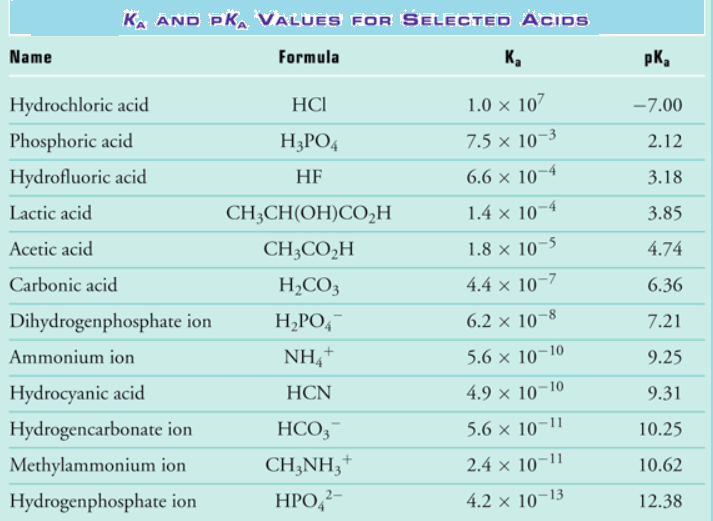
Web determine at a glance the relative strengths of a host of acids and bases. Web acid strengths are normally expressed using p ka values rather than ka values, where the pka is the negative common logarithm of the ka: The acid and base in a given row are conjugate to each other. If the ionization reaction is essentially complete, the acid or base is termed strong; Web figure 15.3.3 lists a series of acids and bases in order of the decreasing strengths of the acids and the corresponding increasing strengths of the bases. Examples of strong acids are hydrochloric acid. A weak acid does not completely ionize in water, yielding only small amounts of \(\ce{h3o+}\) and \(\ce{a^{−}}\). Pka = −log ka p k a = − log k a. Web the strength of acids and bases, i.e., the extent of dissociation of the dissolved acid or base into ions in water is described. Web definitions of ph, poh, and the ph scale. Web chart of acid and base strength. Web the relative strength of an acid or base is the extent to which it ionizes when dissolved in water. The dissociation of a strong acid in solution is effectively complete, except in its most concentrated solutions. (select option to see volume pricing availability) 8½ × 11, pad of 30 (ap7229) $24.50. Table \(\pageindex{1}\) lists several strong acids.
The Strength Of Acids And Bases Is Determined By Their Ability To Donate Or Accept Protons (H Ions) And Can Be Quantified Using The Concepts Of Dissociation In Water And The Corresponding Equilibrium Constants.
The terms strong and weak describe the ability of acid and base solutions to conduct electricity. The strong bases are listed at the bottom right of the table and get weaker as we move to the top of the table. Chart or notebook size available. The first six acids in figure 15.3.3 are the most common strong acids.
Web The Strength Of Acids And Bases, I.e., The Extent Of Dissociation Of The Dissolved Acid Or Base Into Ions In Water Is Described.
If relatively little ionization occurs, the acid or base is weak. Look at where the negative charge ends up in each conjugate base. Web a strong acid yields 100% (or very nearly so) of \(\ce{h3o+}\) and \(\ce{a^{−}}\) when the acid ionizes in water. Web a reactivity series, or acid strength chart, provides a visual representation of the relative strength of various acids.
Even If You’re Not A Chemist, You’ll Doubtless Remember Learning About Acids Back In School.
The acid and base in a given row are conjugate to each other. By andy brunning september 28, 2016. If the acid or base conducts electricity strongly, it is a strong acid or base. For each acid, the ionization reaction shows the acid’s conjugate base.
Web The Relative Strength Of An Acid Or Base Is The Extent To Which It Ionizes When Dissolved In Water.
The first six acids in figure 14.3.3 are the most common strong acids. Web the terms strong and weak give an indication of the strength of an acid or base. Web acid strengths are normally expressed using p ka values rather than ka values, where the pka is the negative common logarithm of the ka: Acid strength increases down a group and increases from left to right across a period.