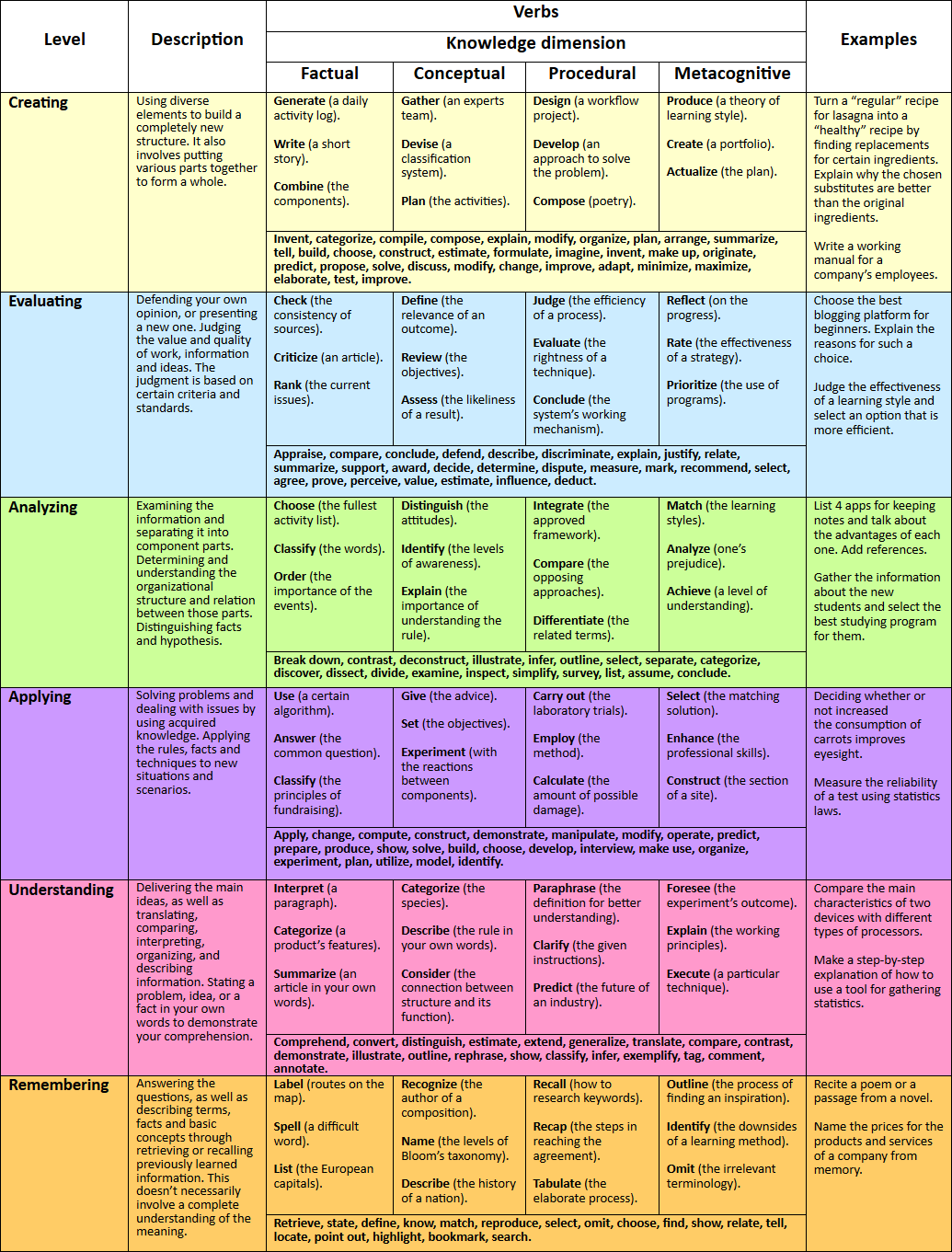
Web comparing, translating, interpreting, giving descriptions, and stating main ideas. Web solve problems to new situations by applying acquired knowledge, facts, techniques and rules in a different way. The following is a list of measurable action verbs that can be used when you are creating your learning objectives. Appraise, argue, assess, attach, choose compare, defend estimate, judge, predict, rate, core, select, support, value, evaluate. Web the chart below arranges bloom's levels of cognitive activity from simple to complex and lists verbs that correspond to each level.
The theory is based upon the idea that there are levels of observable actions that indicate something is happening in the brain (cognitive activity.) Before we unleash the power of these verbs, a quick refresher on bloom’s taxonomy is in order. Web revised bloom's taxonomy chart. Generating new ideas, products, or ways of viewing things. Associate with assume responsibility believe in be convinced give hold select show interest.
Generating new ideas, products, or ways of viewing things. The theory is based upon the idea that there are levels of observable actions that indicate something is happening in the brain (cognitive activity.) by creating learning objectives using. Associate with assume responsibility believe in be convinced give hold select show interest. The theory is based upon the idea that there are levels of observable actions that indicate something is happening in the brain (cognitive activity.) The following is a list of measurable action verbs that can be used when you are creating your learning objectives.
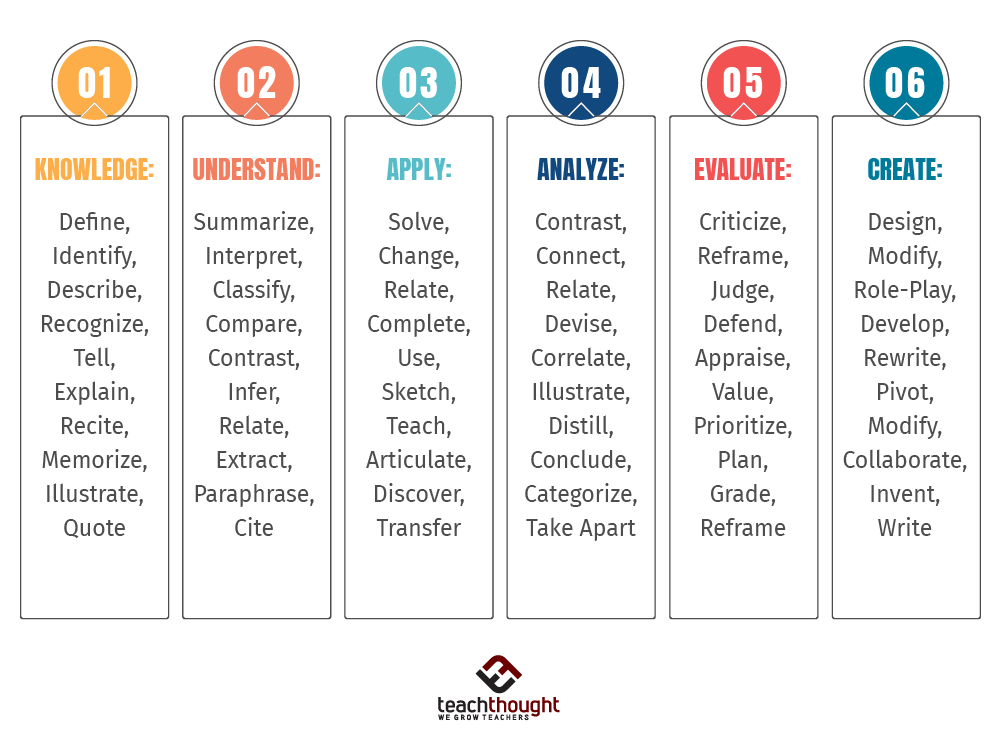
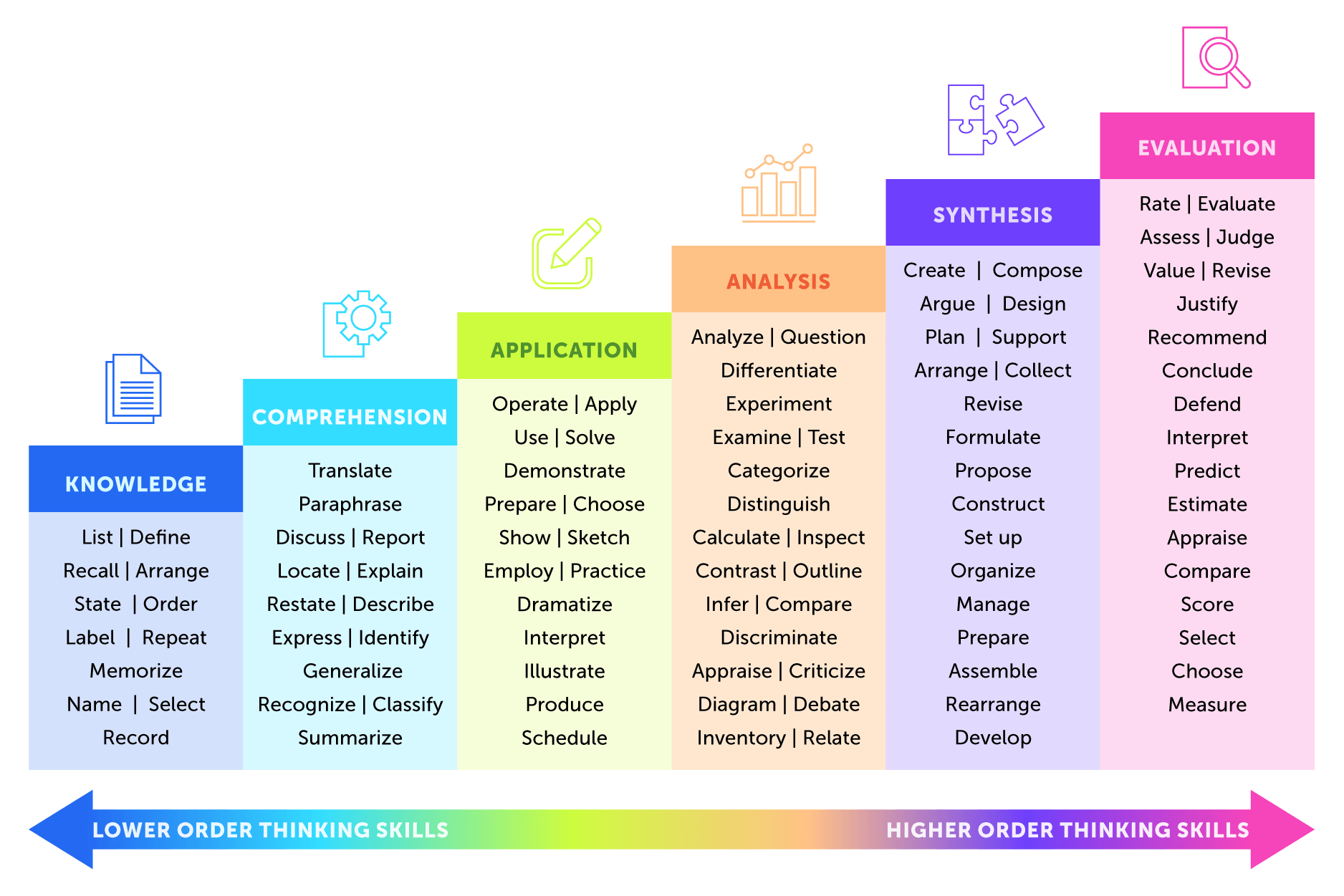
Web benjamin bloom created a taxonomy of measurable verbs to help us describe and classify observable knowledge, skills, attitudes, behaviors and abilities. Each of the three categories requires learners to use different sets of mental processing to achieve stated outcomes within a learning situation. Use the chart to help formulate effective learning objectives for your educational events. Make inferences and find evidence to support generalizations. Solve problems to new situations by applying acquired knowledge, facts, techniques and rules in a different way. Discover a list of action verbs that you can use to form learning objectives. Web revised bloom's taxonomy chart. Web comparing, translating, interpreting, giving descriptions, and stating main ideas. In 1956, benjamin bloom with collaborators max englehart, edward furst, walter hill, and david krathwohl published a framework for categorizing educational goals: Web what is bloom’s taxonomy? Web read on and dive into over 200 bloom’s taxonomy verbs that can change the way you frame learning objectives and guide students toward success! Web bloom’s taxonomy is a hierarchical model of cognitive skills in education, developed by benjamin bloom in 1956. Designing, constructing, planning, producing, inventing. Remembering, understanding, applying, analyzing, evaluating, and creating. Knowledge, comprehension, application, analysis, synthesis, and evaluation.
It Categorizes Learning Objectives Into Six Levels, From Simpler To More Complex:
Web solve problems to new situations by applying acquired knowledge, facts, techniques and rules in a different way. This assists instructors when creating lesson and course objectives. These questions are not bad, but using them all the time is. Act change behavior develop code of behavior develop philosophy.
Web Read On And Dive Into Over 200 Bloom’s Taxonomy Verbs That Can Change The Way You Frame Learning Objectives And Guide Students Toward Success!
Web what is bloom’s taxonomy? Remembering, understanding, applying, analyzing, evaluating, and creating. Web comparing, translating, interpreting, giving descriptions, and stating main ideas. Web bloom’s taxonomy provides a list of action verbs based on each level of understanding.
Web Revised Bloom's Taxonomy Chart.
Designing, constructing, planning, producing, inventing. Generating new ideas, products, or ways of viewing things. Web summary of the revised version of bloom’s taxonomy with verbs for writing learning objectives at all levels of the cognitive, affective, and psychomotor domains. Web additional information about bloom’s revised taxonomy is available here:
These Verbs May Also Be Considered Beyond The Realm Of Cognitive Tasks In The Domains Of Affective And Psychomotor Learning (Harrow, 1972;
Make inferences and find evidence to support generalizations. Examine and break information into parts by identifying motives or causes. Web the following tables offer a list of verbs representing a hierarchy of learning levels from basic knowledge to the highest level of creativity. Web bloom's taxonomy verbs include evaluate:



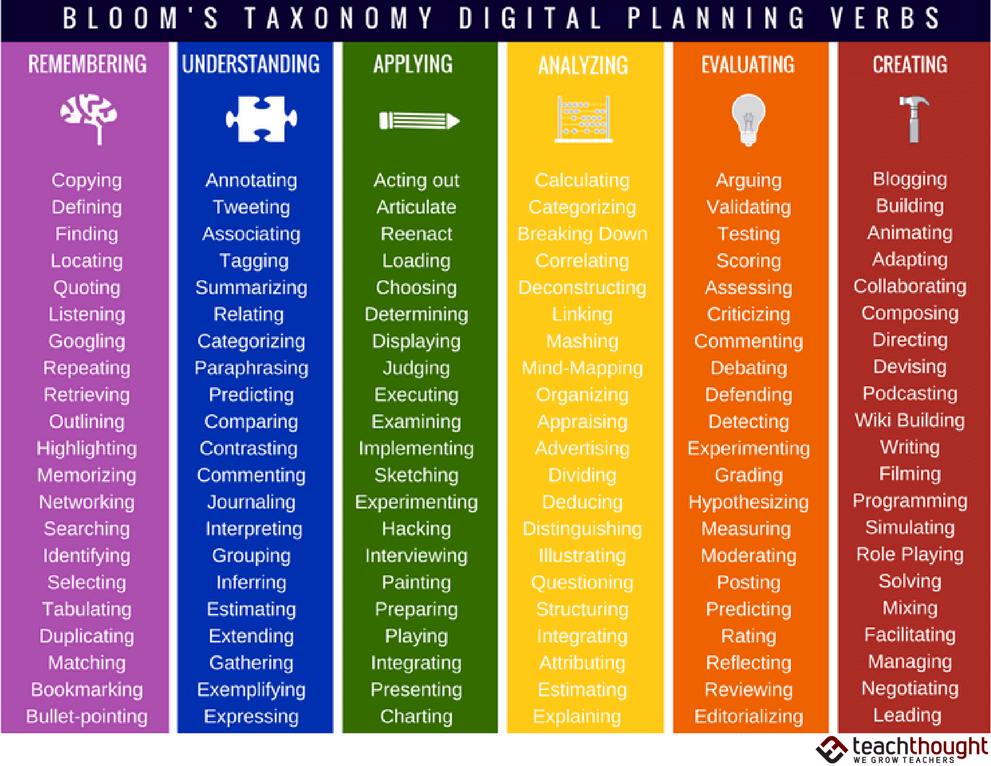
![Bloom's Digital Taxonomy Verbs [Infographic] 36239971987237262](https://i.pinimg.com/originals/da/ad/23/daad23c649df8a68ecd9d4f5bad049bd.png)