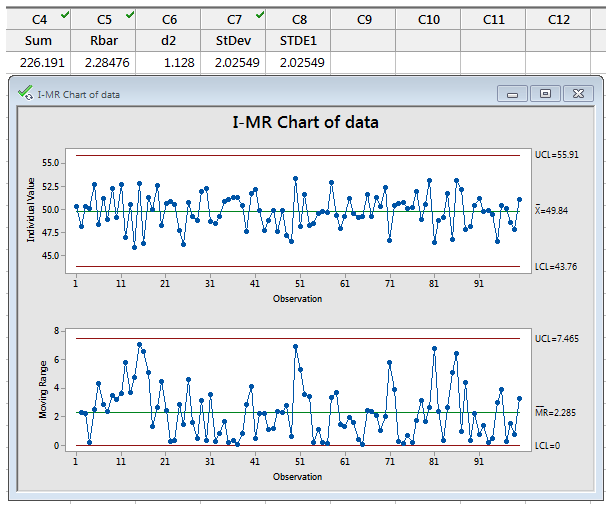
When you change an unstable process,. If the calculated control limit is farther from the center line than the value that you specify, minitab displays the bound. Lower control limit (lcl) upper control limit (ucl) notation. This is then where you get a negative control limit. The calculated average is then.
1) the mr chart provides redundant information and is not necessary. Select the method or formula of your choice. If the calculated control limit is farther from the center line than the value that you specify, minitab displays the bound. The median moving range is impacted much less by large moving range values than the average. Draw the average line on the moving range chart.
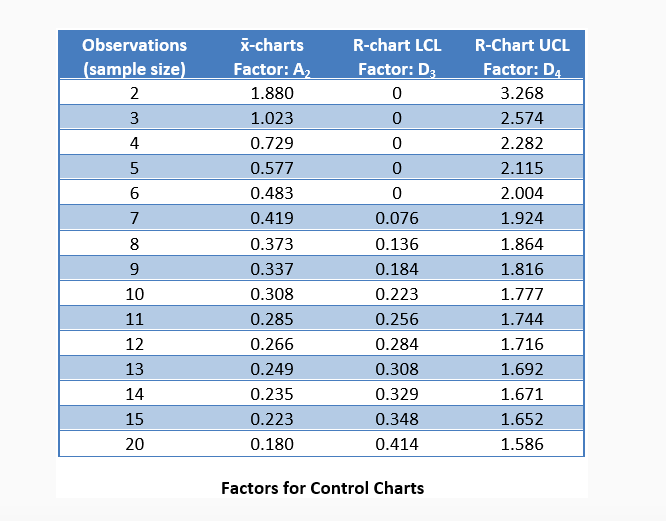
To calculate the upper control limit, multiply the average moving range, , by. If the calculated control limit is farther from the center line than the value that you specify, minitab displays the bound. Calculate the control limits for the moving range chart 1. When you change an unstable process,. 95% or 99% of data should fall within ucl and lcl.
One method is to use the median moving range. The median moving range is impacted much less by large moving range values than the average. In some measures, that’s not a practical value, like in the example below. Lcl line shows the lower control limit. This newsletter has examined when to calculate control limits when you first start a control chart. We know that defects cannot be less than zero (that is. The average moving range, , of length w is given by. Where mri is the moving. Calculate the control limits for the moving range chart 1. To calculate the upper control limit, multiply the average moving range, , by. The average moving range, , of length w is given by the following formula: Determining whether a process is stable and ready to be improved. If the lcl comes out negative in calculation, then there is no lower control limit and lcl is considered to be zero. This is receiving further discussion here. Draw the average line on the moving range chart.
To Calculate The Upper Control Limit, Multiply The Average Moving Range, , By.
The control chart xmr consists of two charts: That is, anything unusual in the mr chart is also apparent in the i chart. If the calculated control limit is farther from the center line than the value that you specify, minitab displays the bound. In minitab you can change the lower boundary to requested limit bound.
The Average Moving Range, , Of Length W Is Given By The Following Formula:
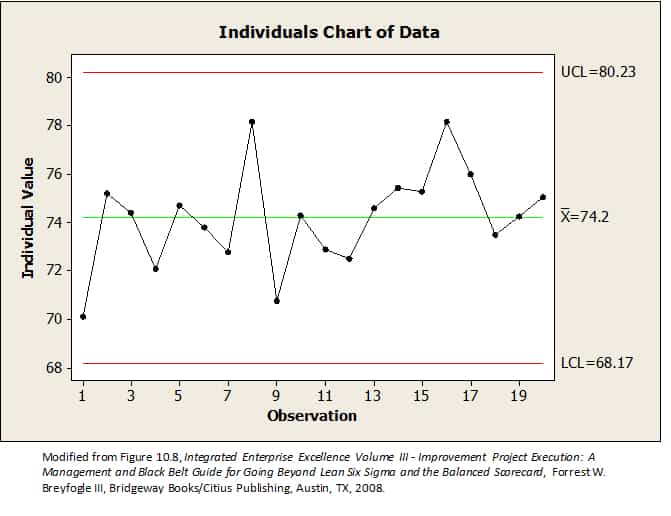
If the lcl comes out negative in calculation, then there is no lower control limit and lcl is considered to be zero. Lower control limit (lcl) the lcl is the greater of the following: Values outside the control limits mark statistically significant changes and may indicate a. Lower control limit (lcl) upper control limit (ucl) notation.
We Know That Defects Cannot Be Less Than Zero (That Is.
Lower control limit (lcl) the lcl is the greater of the following: 95% or 99% of data should fall within ucl and lcl. One method is to use the median moving range. Where mri is the moving.
The Lower Control Limit, Labelled Lcl On The Graph, Indicates That On This Xbar Chart, Any Group Of Five Packages Averaging Under 41.7503G Is An Indication That The Process Is Unstable And Special Cause Variation Exists.
The average moving range, , of length w is given by. Calculate the control limits for the moving range chart 1. As we know sometimes when we calculate the natural process limits, the lower limit is negative. 1) the mr chart provides redundant information and is not necessary.