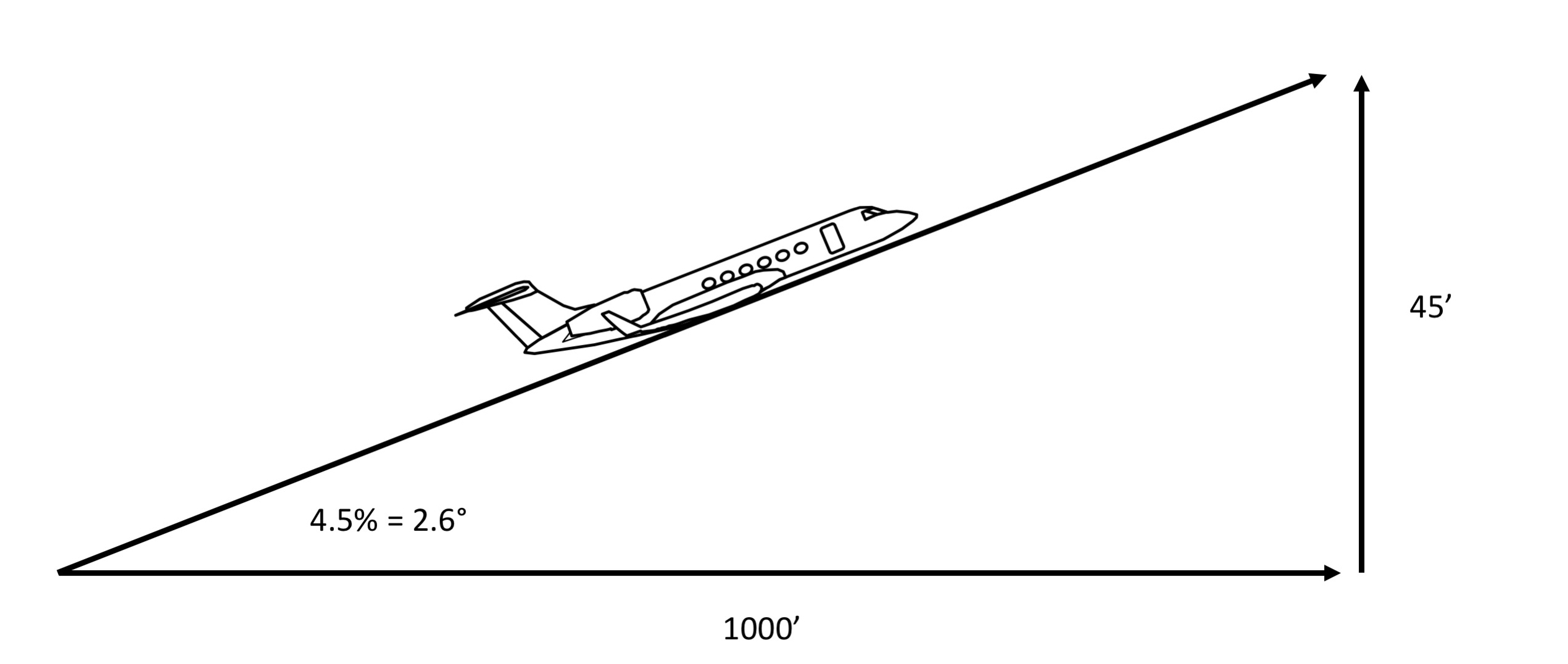
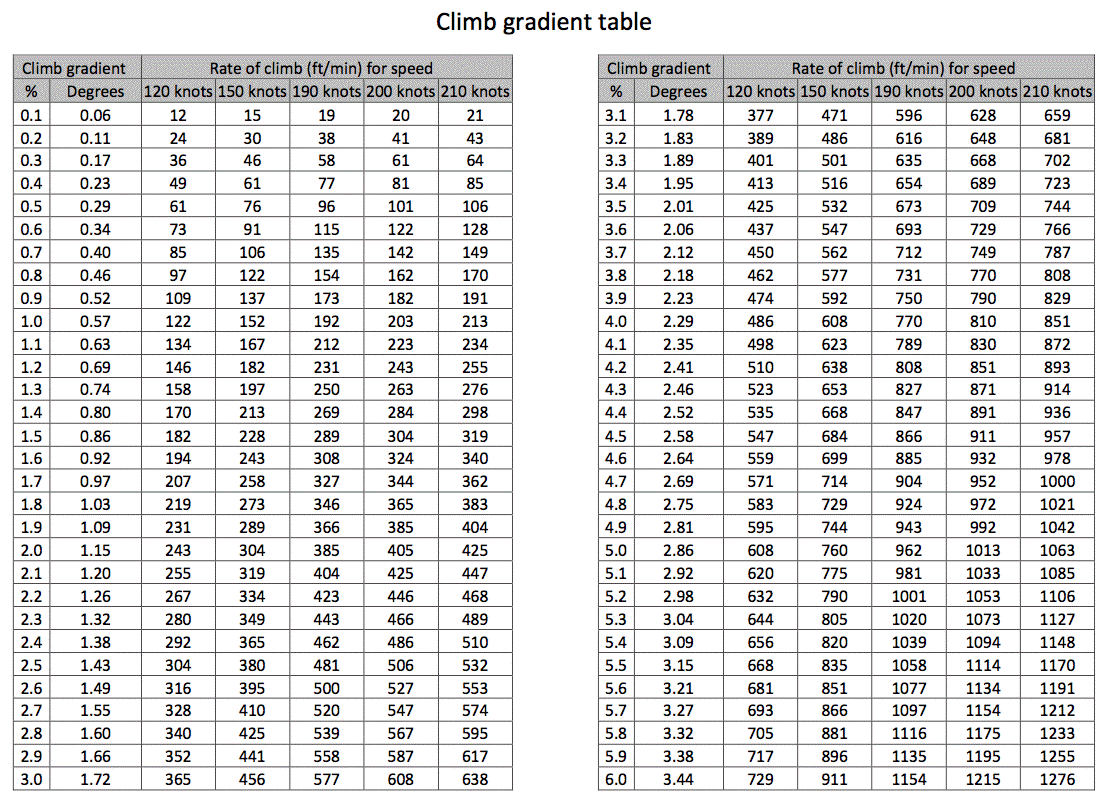
Web learn how to interpret and apply the published climb gradient requirements for ifr departure procedures and missed approaches, and avoid excessive weight. Web 500 feet per nautical mile divided by 6076' (one nautical mile) x 100 will give you the required climb gradient. Within the context of the takeoff flight path, two primary requirements must be met, both predicated on the assumption of. This value is designed to provide 48 feet of clearance at one nautical mile from the departure. Web climb gradient is feet/nm.
Reduced distance to climb to the. Web it represents the minimum rate of climb required to safely clear obstacles and terrain during departure. Web you cannot look at your aircraft's ground speed, such as 150 knots, and find your climb gradient from this chart. Web climb gradient is feet/nm. Within the context of the takeoff flight path, two primary requirements must be met, both predicated on the assumption of.
This web page does not contain. Web the biggest difference, besides the location, is the jepp chart converts climb gradient into a useable number. Max excess thrust results in the best angle of climb; Web dive deep into climb gradients for ifr departures, learn how to calculate and explore their significance in flight planning. The 684 number is a climb rate, a very different.
The obstacle environment beyond the runway may require a climb gradient greater than. However, we are also required to accelerate to a speed called vfs (final segment climb speed). Web dive deep into climb gradients for ifr departures, learn how to calculate and explore their significance in flight planning. Within the context of the takeoff flight path, two primary requirements must be met, both predicated on the assumption of. Web it represents the minimum rate of climb required to safely clear obstacles and terrain during departure. Web climb gradient is feet/nm. Web you cannot look at your aircraft's ground speed, such as 150 knots, and find your climb gradient from this chart. This web page does not contain. This value is designed to provide 48 feet of clearance at one nautical mile from the departure. Web 500 feet per nautical mile divided by 6076' (one nautical mile) x 100 will give you the required climb gradient. The 684 number is a climb rate, a very different. This table is for use in. Notice on the jepp chart, 260′ per nm translates into. Web the climb gradient is now half of what it was before: Occurs below l/dmax for a prop;
Web When Using Climb Gradient Tables, You Can Find The Required Climb Gradient For A Specific Departure Procedure Based On Factors Such As Ground Speed And Nautical.
The obstacle environment beyond the runway may require a climb gradient greater than. Web climb gradient is feet/nm. Web the climb gradient is the percentage of the rise over run (100% if you are climbing at 45 degrees) that your aircraft is climbing at while the rate of climb is the speed at which you. Occurs at l/dmax for a jet;
However, We Are Also Required To Accelerate To A Speed Called Vfs (Final Segment Climb Speed).
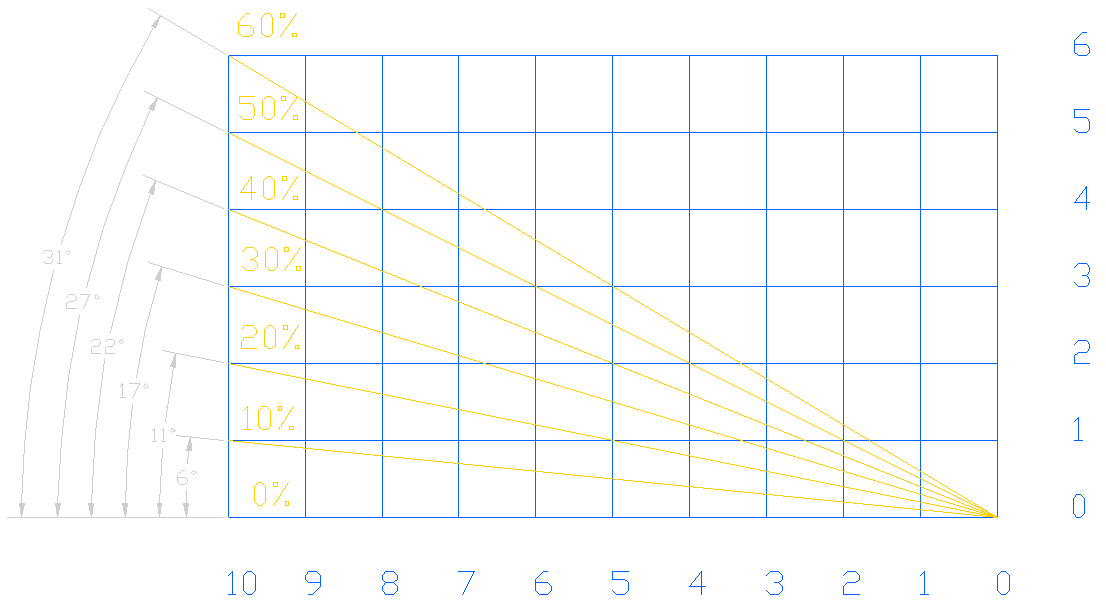
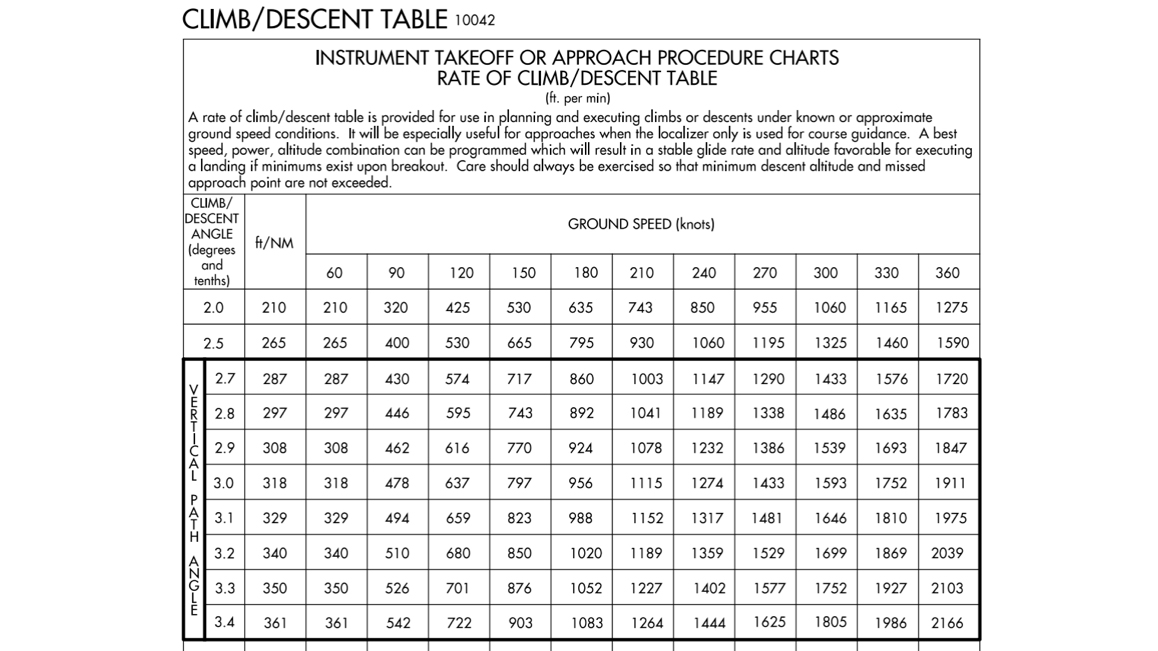
This web page does not contain. Web 500 feet per nautical mile divided by 6076' (one nautical mile) x 100 will give you the required climb gradient. Web chart a maximum climb gradient based on a plane evaluated throughout the sid for the most restrictive atc restriction or terps requirement. Web this table provides a rate of climb or descent in feet per minute below the groundspeed in knots for the gradient shown in percent (%) at the left.
Web Takeoff Segments And Climb Requirements.
Web dive deep into climb gradients for ifr departures, learn how to calculate and explore their significance in flight planning. Max excess thrust results in the best angle of climb; This value is designed to provide 48 feet of clearance at one nautical mile from the departure. Web you cannot look at your aircraft's ground speed, such as 150 knots, and find your climb gradient from this chart.
This Table Is For Use In.
Notice on the jepp chart, 260′ per nm translates into. Web furthermore, the oei second segment climb gradient (net or gross as chosen by the manufacturer) that is published in the afm is intended for use on the oei. Reduced distance to climb to the. 500/6076x100= 8.23% take your gradient times your.