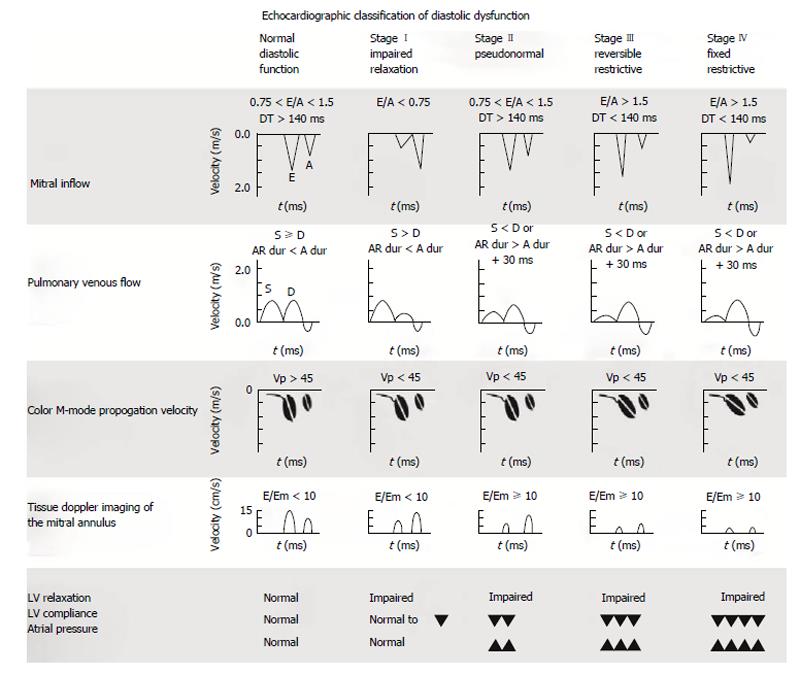
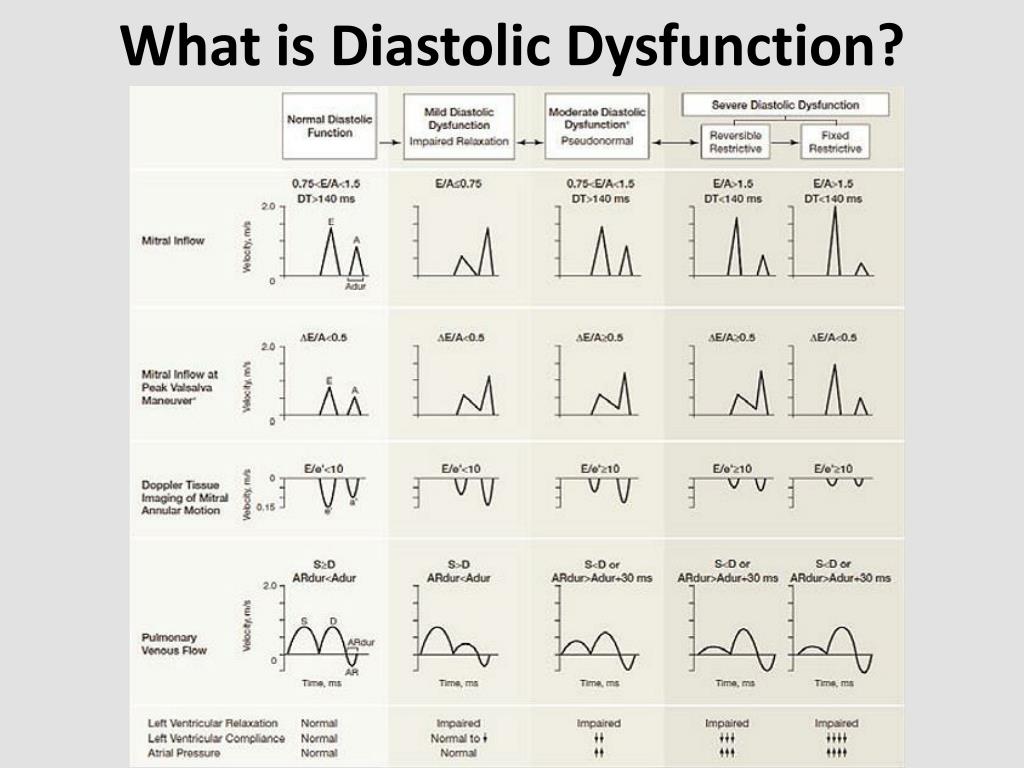
1 in contrast, an abnormal filling pattern and progressively greater abnormalities of left filling (impaired relaxation versus pseudonormalized and restricted filling patterns) indicate patients with a progressively increased risk of subsequent mortality. Mitral inflow, tissue doppler, pulmonic vein flow, tricuspid regurgitation velocity, deceleration time, isometric volumetric time, and more. In pts with normal lvef≥ 50%. Web in certain clinical situations, conventional echo indices cannot be readily applied to assess diastolic dysfunction. Web in patients with heart failure and reduced ef (hfref), the main goal is to estimate lv filling pressures and grade the degree of diastolic dysfunction (diastolic dysfunction is presumed to be present in these patients) based on the parameters presented below and the algorithm in figure 8b.
Diastolic dysfunction is a problem with diastole, the first part of your heartbeat. In pts with normal lvef≥ 50%. During diastole, your lower heart chambers (ventricles) relax as they fill with blood. Blood flow across the mitral valve. Web in certain clinical situations, conventional echo indices cannot be readily applied to assess diastolic dysfunction.
Web criteria for diagnosis of lv diastolic dysfunction in patients with normal lvef in jase 2016. Blood flow across the mitral valve. Web diastolic dysfunction is when the heart’s ventricles abnormally stiffen, which prevents the ventricles from relaxing as they should and prevents them from filling up. Web in certain clinical situations, conventional echo indices cannot be readily applied to assess diastolic dysfunction. 1 in contrast, an abnormal filling pattern and progressively greater abnormalities of left filling (impaired relaxation versus pseudonormalized and restricted filling patterns) indicate patients with a progressively increased risk of subsequent mortality.
During diastole, your lower heart chambers (ventricles) relax as they fill with blood. The following section provides recommendations on assessing diastolic function in this group of patients. Web diastolic function can be estimated from e/a ratio, e’ and deceleration time (dt). Web in patients with heart failure and reduced ef (hfref), the main goal is to estimate lv filling pressures and grade the degree of diastolic dysfunction (diastolic dysfunction is presumed to be present in these patients) based on the parameters presented below and the algorithm in figure 8b. Web in certain clinical situations, conventional echo indices cannot be readily applied to assess diastolic dysfunction. Web criteria for diagnosis of lv diastolic dysfunction in patients with normal lvef in jase 2016. Web just look at what the american society of echocardiography (ase) guidelines on what you should measure: Web diastolic dysfunction is when the heart’s ventricles abnormally stiffen, which prevents the ventricles from relaxing as they should and prevents them from filling up. Diastolic dysfunction may occur when your ventricles are stiff and don’t relax properly. 1 in contrast, an abnormal filling pattern and progressively greater abnormalities of left filling (impaired relaxation versus pseudonormalized and restricted filling patterns) indicate patients with a progressively increased risk of subsequent mortality. These three methods, as well as several supplementary methods, will now be discussed in detail. Mitral inflow, tissue doppler, pulmonic vein flow, tricuspid regurgitation velocity, deceleration time, isometric volumetric time, and more. This disrupts the flow of blood to and from the organs of the body. Web although diastolic heart failure is clinically and radiographically indistinguishable from systolic heart failure, normal ejection fraction and abnormal diastolic function in the presence of. In pts with normal lvef≥ 50%.
Diastolic Dysfunction Is A Problem With Diastole, The First Part Of Your Heartbeat.
In pts with normal lvef≥ 50%. Web echocardiographic assessment of lv filling pressures and diastolic dysfunction grade. The following section provides recommendations on assessing diastolic function in this group of patients. Web in certain clinical situations, conventional echo indices cannot be readily applied to assess diastolic dysfunction.
Diastolic Dysfunction May Occur When Your Ventricles Are Stiff And Don’t Relax Properly.
Web just look at what the american society of echocardiography (ase) guidelines on what you should measure: Web diastolic dysfunction is when the heart’s ventricles abnormally stiffen, which prevents the ventricles from relaxing as they should and prevents them from filling up. Mitral inflow, tissue doppler, pulmonic vein flow, tricuspid regurgitation velocity, deceleration time, isometric volumetric time, and more. Web criteria for diagnosis of lv diastolic dysfunction in patients with normal lvef in jase 2016.
Web Although Diastolic Heart Failure Is Clinically And Radiographically Indistinguishable From Systolic Heart Failure, Normal Ejection Fraction And Abnormal Diastolic Function In The Presence Of.
1 in contrast, an abnormal filling pattern and progressively greater abnormalities of left filling (impaired relaxation versus pseudonormalized and restricted filling patterns) indicate patients with a progressively increased risk of subsequent mortality. Web diastolic function can be estimated from e/a ratio, e’ and deceleration time (dt). This disrupts the flow of blood to and from the organs of the body. During diastole, your lower heart chambers (ventricles) relax as they fill with blood.
These Three Methods, As Well As Several Supplementary Methods, Will Now Be Discussed In Detail.
Blood flow across the mitral valve. Web in patients with heart failure and reduced ef (hfref), the main goal is to estimate lv filling pressures and grade the degree of diastolic dysfunction (diastolic dysfunction is presumed to be present in these patients) based on the parameters presented below and the algorithm in figure 8b.