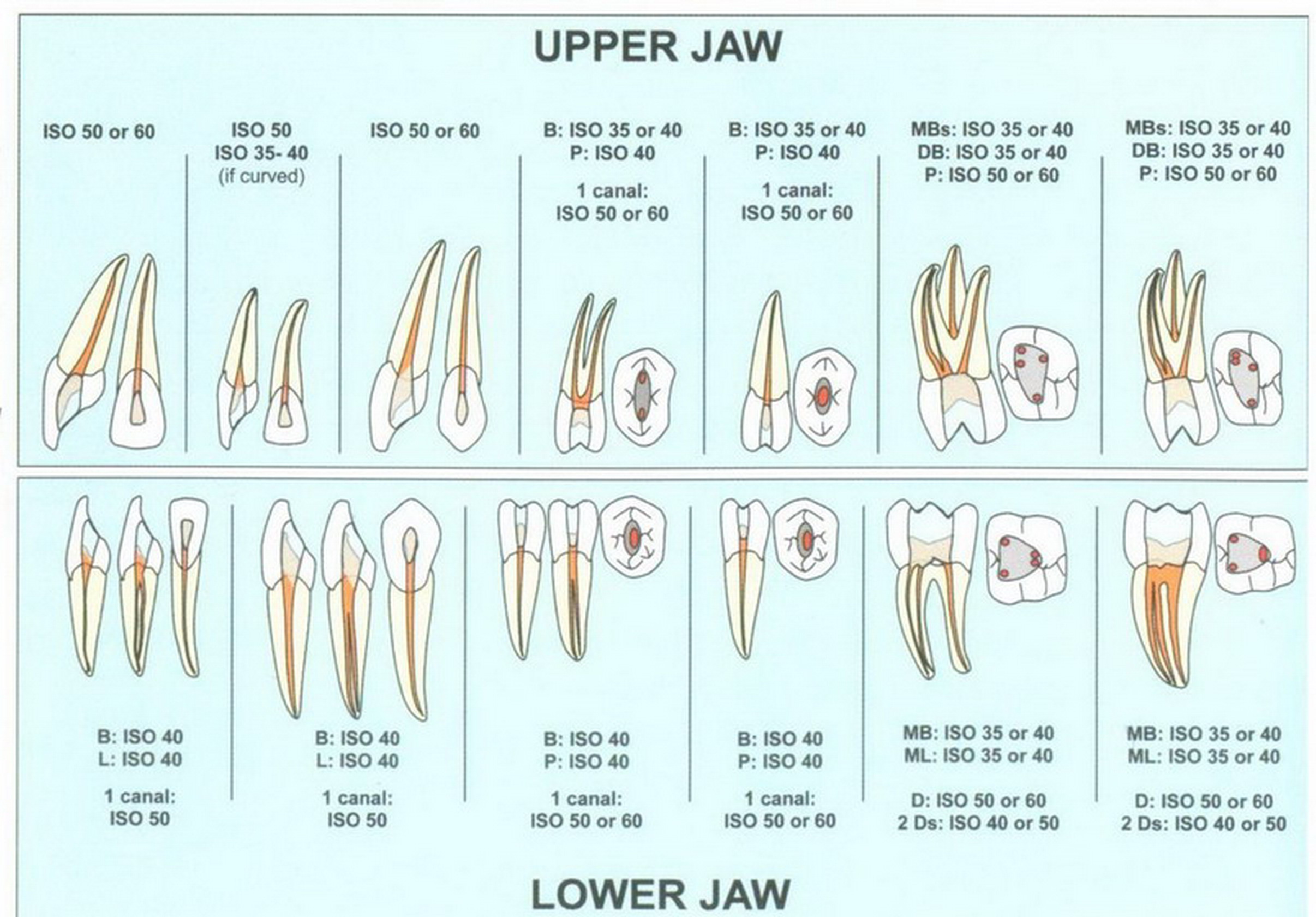
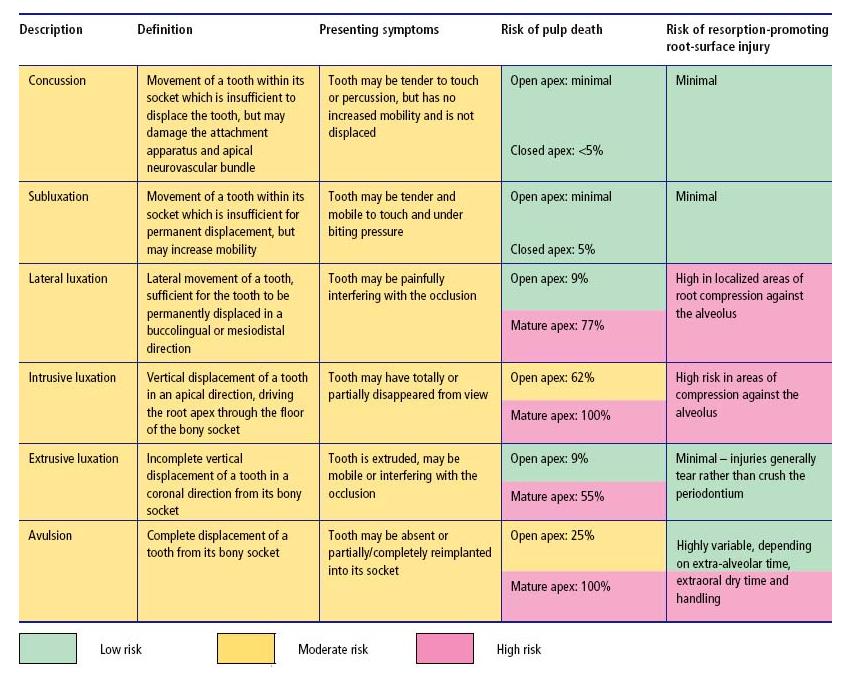
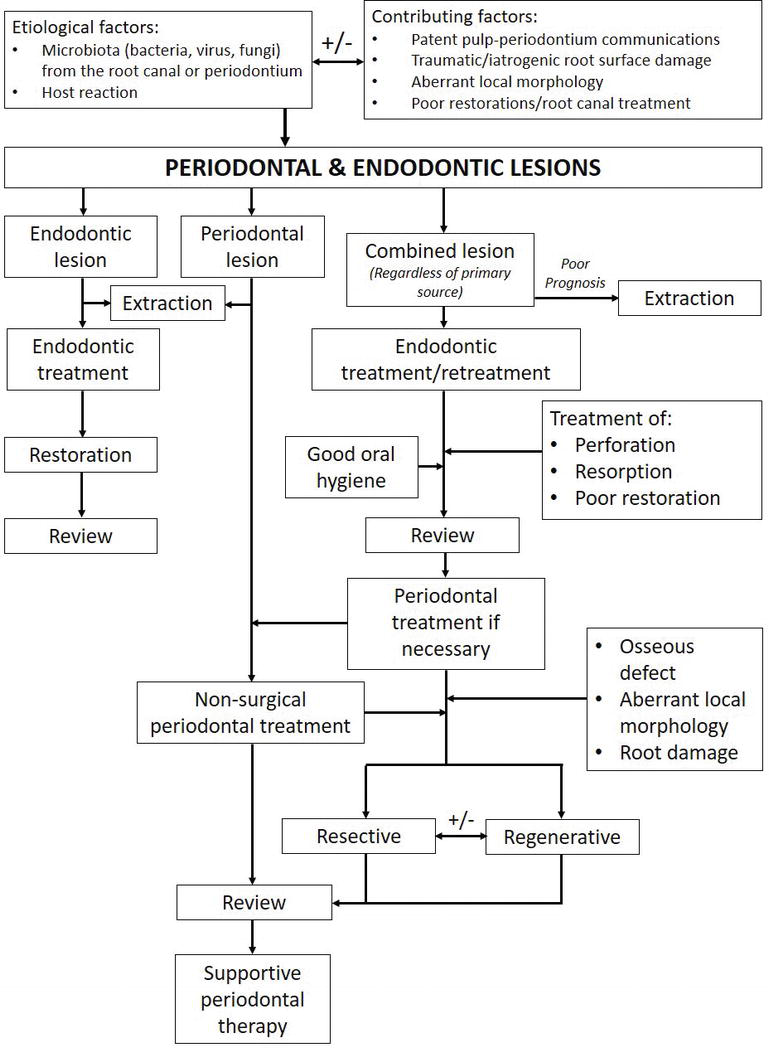
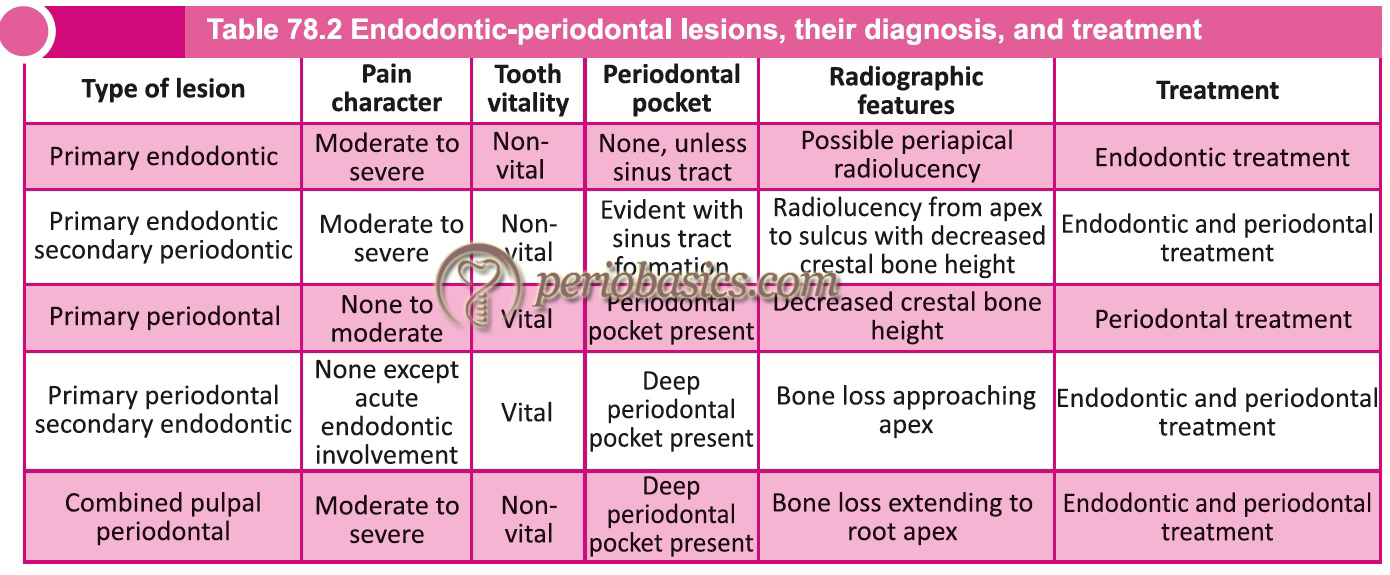
Although it can be frustrating for the patient and the provider, sometimes no treatment until the. And if you’d like a little more support right this minute—grab my free diagnostic checklist , print it out, and put it to good use starting today! (click here for full size image) this guide is by no means comprehensive, but should serve as a flowchart for the practitioner and help aid in reaching a diagnosis. Recognize when orofacial pain and infections are not of endodontic origin. Launch the treatment options guide.
View the treatment options guide now or purchase copies from the aae online store. Understanding both the pulpal and periradicular diagnoses and how to obtain them are crucial. Web an endodontic diagnosis has two components: The following is a list of possible pulpal diagnoses and how they are defined by pulpal symptoms and findings. Pulpal diagnosis is the clinical condition of the pulp, as evaluated by ice, cold and electric pulp test assessments.
Web clinical diagnostic category indicating that the tooth has been previously treated by partial endodontic therapy (eg, pulpotomy, pulpectomy). Duration—does pain linger after the stimulus is removed? Identify conditions for which root canal treatment is indicated and contraindicated; Pulpal diagnosis indicates the status of the pulp (nerve and connective tissue inside the tooth) and can be accomplished by using thermal and electric pulp tests. A pulpal diagnosis, which indicates the status of the pulpal (nerve & connective tissue inside the tooth), and a periapical diagnosis, which indicates the status of the periapex (tissue around the end of the root).
Web as previously described, endodontic diagnosis is composed of two parts. View the treatment options guide now or purchase copies from the aae online store. Teeth with normal periradicular tissues that are not sensitive to percussion or palpation testing. Web a proper endodontic diagnosis is imperative to identify the offending tooth that is causing the patient’s symptoms and/or disease. Web a careful evaluation of the patient’s clinical presentation and pathosis is key to establishing a sound endodontic diagnosis. Web in order to render proper treatment, a complete endodontic diagnosis must include both a pulpal and a periapical diagnosis for each tooth evaluated. Web it’s all about doing better endo, from diagnosis all the way to the final obturation. This system will help clinicians understand the progressive nature of pulpal and periapical disease, and guide them to the most appropriate treatment. Intensity—the more the pain disrupts the patient's lifestyle, the more likely it is caused by irreversible pathosis. Launch the treatment options guide. Pulpal diagnosis is the clinical condition of the pulp, as evaluated by ice, cold and electric pulp test assessments. Duration—does pain linger after the stimulus is removed? (click here for full size image) this guide is by no means comprehensive, but should serve as a flowchart for the practitioner and help aid in reaching a diagnosis. Extraoral and intraoral examinations, along with periodontal and radiographic assessments, are key steps in the overall diagnostic process. Web clinical diagnostic category indicating that the tooth has been previously treated by partial endodontic therapy (eg, pulpotomy, pulpectomy).
Web Endodontic Diagnosis Can Be Challenging.
Stimulus—pulp tests should be chosen based upon what provokes the patient's chief complaint. Web an endodontic decision tree can help you understand in broad strokes the basic signs and symptoms utilized to determine if root canal treatment is necessary. Pulpal diagnosis and the periapical diagnosis. This system will help clinicians understand the progressive nature of pulpal and periapical disease, and guide them to the most appropriate treatment.
Intensity—The More The Pain Disrupts The Patient's Lifestyle, The More Likely It Is Caused By Irreversible Pathosis.
Thermal testing provides a lot of pulpal diagnosis information. A pulpal diagnosis, which indicates the status of the pulpal (nerve & connective tissue inside the tooth), and a periapical diagnosis, which indicates the status of the periapex (tissue around the end of the root). Extraoral and intraoral examinations, along with periodontal and radiographic assessments, are key steps in the overall diagnostic process. Web in order to render proper treatment, a complete endodontic diagnosis must include both a pulpal and a periapical diagnosis for each tooth evaluated.
Web Endodontic Diagnosis Is Composed Of Two Parts:
Dental practice acts vary among jurisdictions, as do the scopes of practice. Identify conditions for which root canal treatment is indicated and contraindicated; Web it’s all about doing better endo, from diagnosis all the way to the final obturation. Web in order to render proper treatment, a complete endodontic diagnosis must include both a pulpal and a periapical diagnosis for each tooth evaluated.
Understanding Both The Pulpal And Periradicular Diagnoses And How To Obtain Them Are Crucial.
Pulpal diagnosis indicates the status of the pulp (nerve and connective tissue inside the tooth) and can be accomplished by using thermal and electric pulp tests. Web the endodontic diagnosis consists of a pulpal diagnosis and periapical diagnosis. Launch the treatment options guide. Teeth with normal periradicular tissues that are not sensitive to percussion or palpation testing.