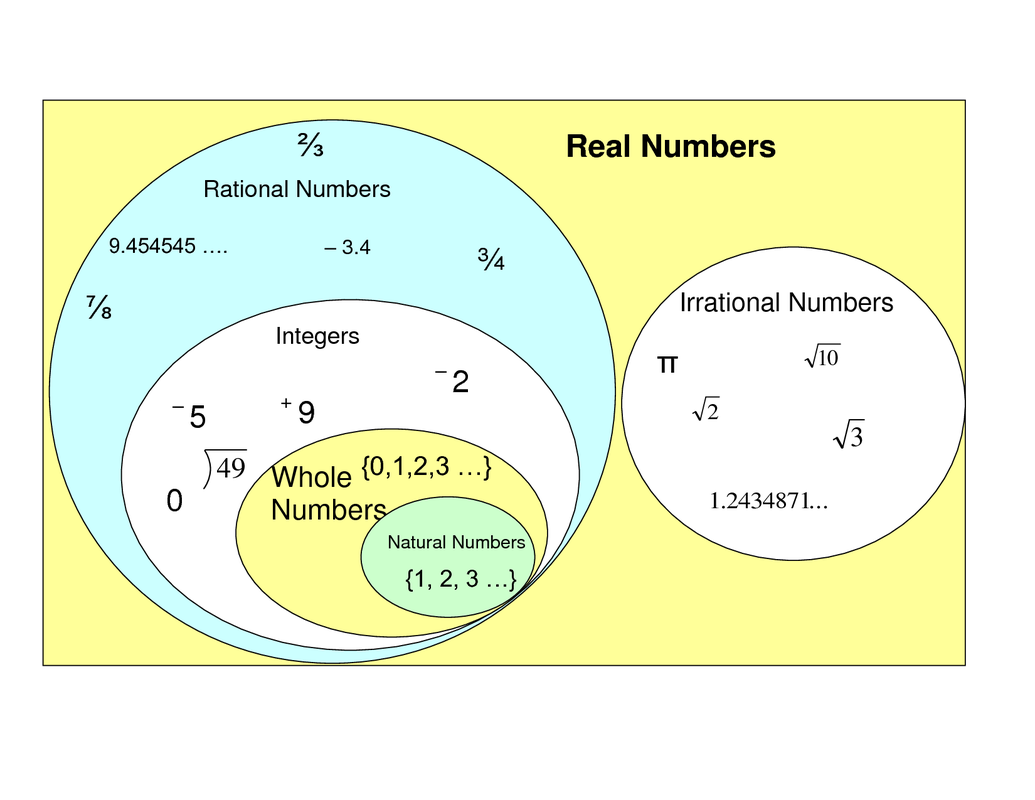
3 is a rational number. For an irrational number x and a rational number y, their product xy = irrational. Web rational numbers, irrational numbers, and roots: There are 5 properties of natural numbers: Web the product of two irrational numbers may or may not be rational.
A few examples of irrational numbers are π , 2 ,. For example, √3 × √3 = 3; Did you know that there's always an irrational number between any two rational numbers? Rational numbers can be expressed as a ratio between two integers. 𝜋=3.14159…, √3=1.73205, euler’s constant, etc.
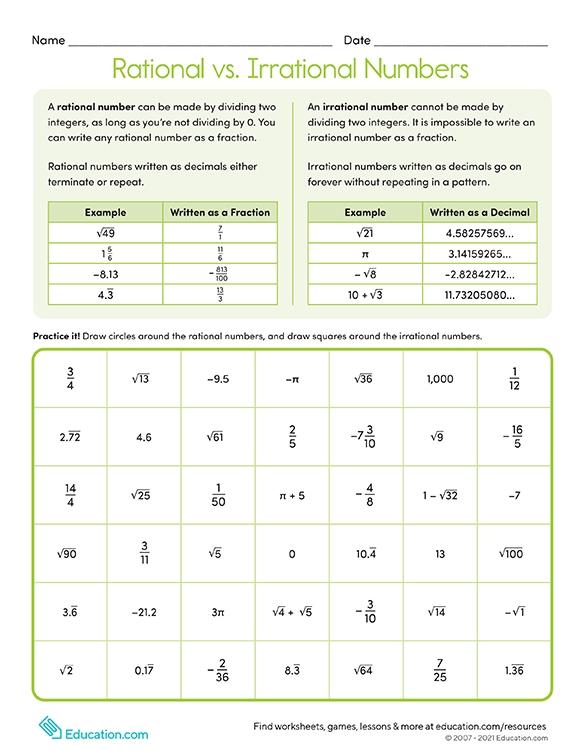
Closure property, commutative property, associative property, identity property and distributive property. The number ½ is a rational number because it is read as integer 1 divided by integer 2. Web determine if the number is rational (r) or irrational (i). If the decimal form of a number. In rational numbers, both numerator and denominator are whole numbers, where the denominator is not equal to zero.
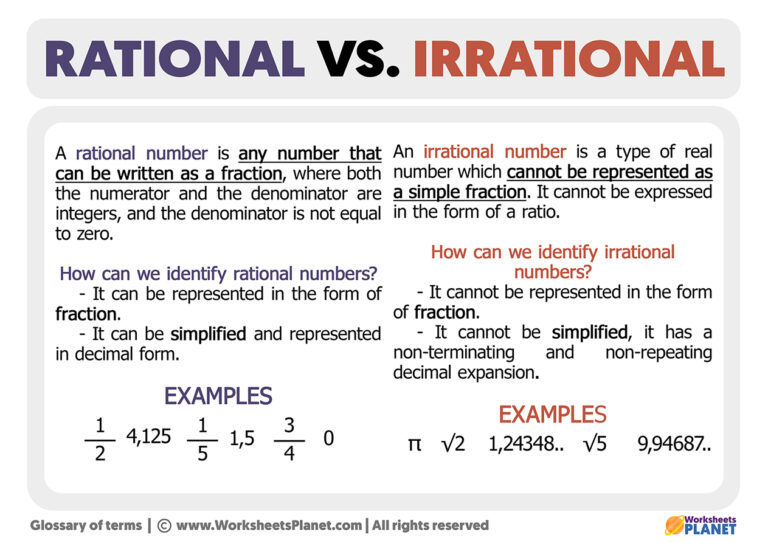
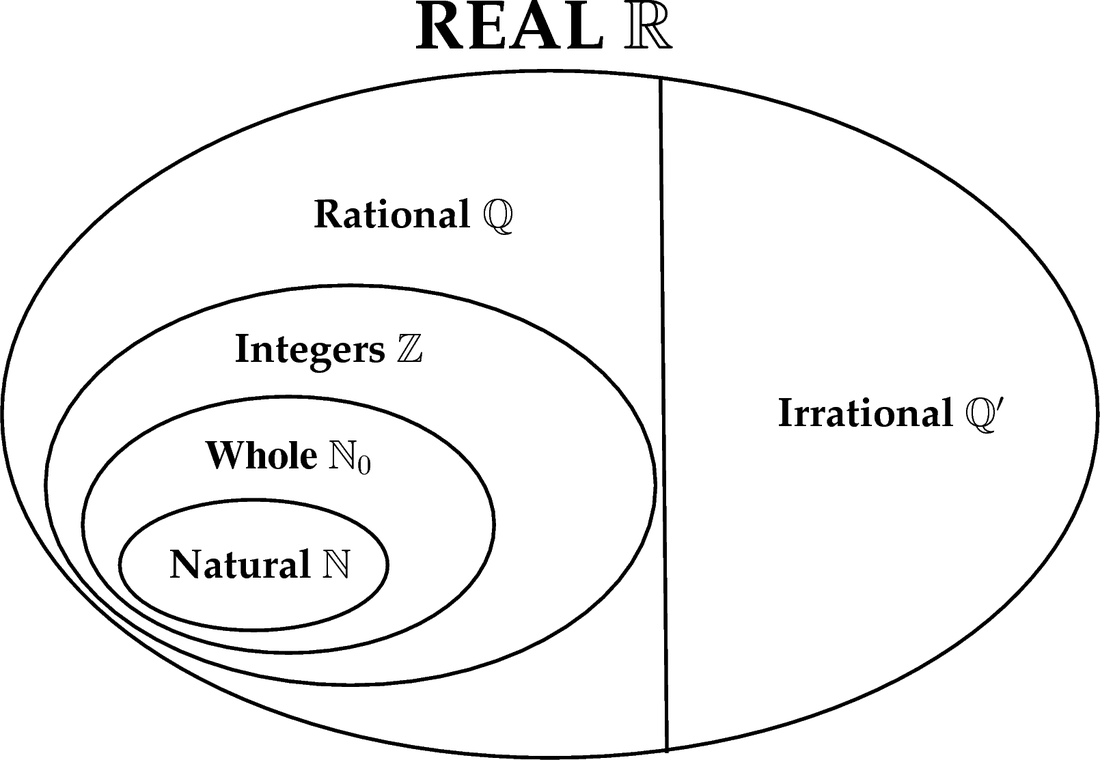
Web rational numbers, irrational numbers, and roots: Learn the differences between rational and irrational numbers explained with definition, differences, solved examples. In rational numbers, both numerator and denominator are whole numbers, where the denominator is not equal to zero. An irrational number is a nonterminating, nonrepeating decimal. A number that cannot be written in the form of a fraction or ratio. Did you know that there's always an irrational number between any two rational numbers? Web a rational number is the one which can be represented in the form of p/q where p and q are integers and q ≠ 0. There are 5 properties of natural numbers: Web an irrational number is a number that cannot be written as the ratio of two integers. But an irrational number cannot be written in the form of simple fractions. The technical definition of an irrational number is that it is a “real number which is not a rational number.” so what does an irrational number look like? Check the chart below, to differentiate between rational and irrational. Its decimal form does not stop and does not repeat. Web for an irrational number x, and a rational number y, their result, x+y = an irrational number. Rational numbers can be written as fractions and ratios.
Check The Chart Below, To Differentiate Between Rational And Irrational.
For example, √3 × √3 = 3; 1.5 is rational, because it can be written as the ratio 3/2. Irrational numbers, when written as a decimal,. Closure property, commutative property, associative property, identity property and distributive property.
Rational Numbers, Irrational Numbers, And Roots:
Its decimal form does not stop and does not repeat. Let's summarize a method we can use to determine whether a number is rational or irrational. All real numbers that are not rational numbers; A number that cannot be written in the form of a fraction or ratio.
Numbers Such As Pi Are Irrational Numbers, As There Is No Ratio Of Integers That Can.
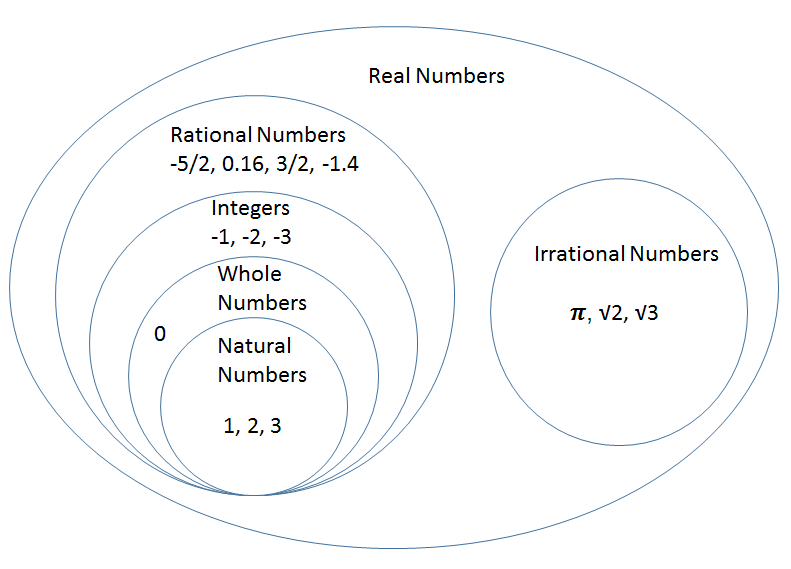
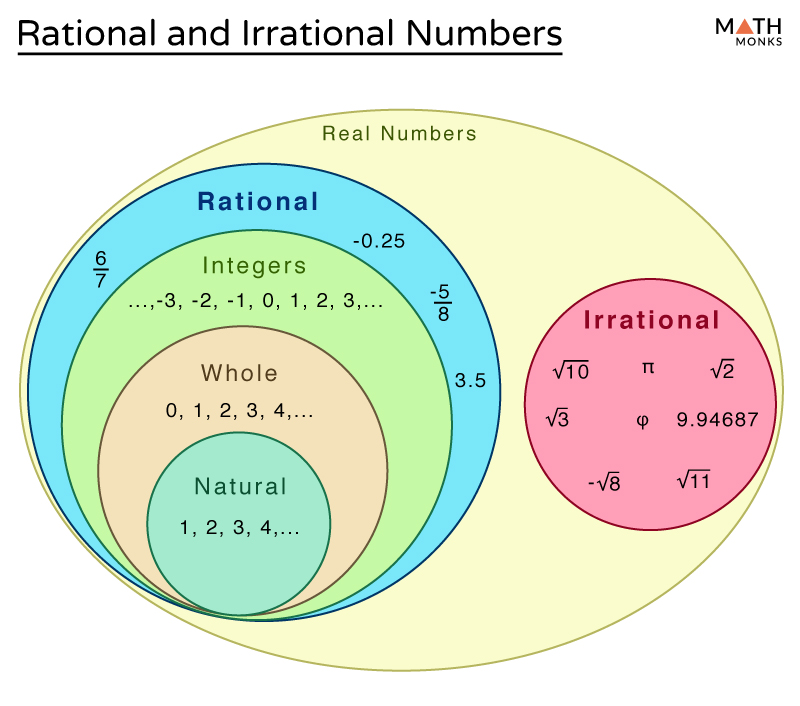
𝜋=3.14159…, √3=1.73205, euler’s constant, etc. The definitions followed by examples are as follows: When any irrational numbers multiplied by any nonzero rational number, their product is an irrational number. All the numbers that can be found on a number line.
A Few Examples Of Irrational Numbers Are Π , 2 ,.
In rational numbers, both numerator and denominator are whole numbers, where the denominator is not equal to zero. Web in your own words, explain the difference between a rational number and an irrational number. There are 5 properties of natural numbers: The technical definition of an irrational number is that it is a “real number which is not a rational number.” so what does an irrational number look like?