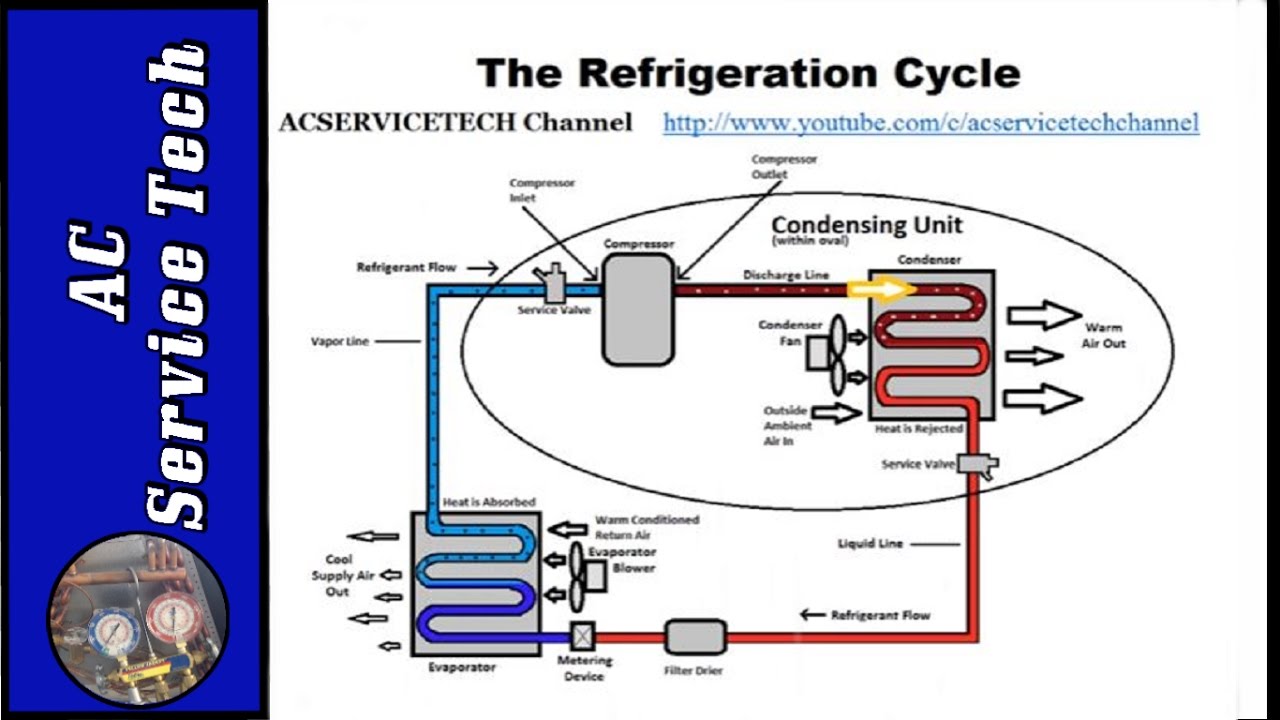
You will find the chart that summarizes all total superheats further on. We are usually looking for 7°f to 15°f superheat. Web the superheat chart includes target ac superheat for 55°f to 128°f outdoor temperature (db temperature) and for 50°f to 76°f indoor evaporator temperature (wb temperature). Subtract the liquid line temperature from the saturation temperature. Web hvac app to calculate superheat.
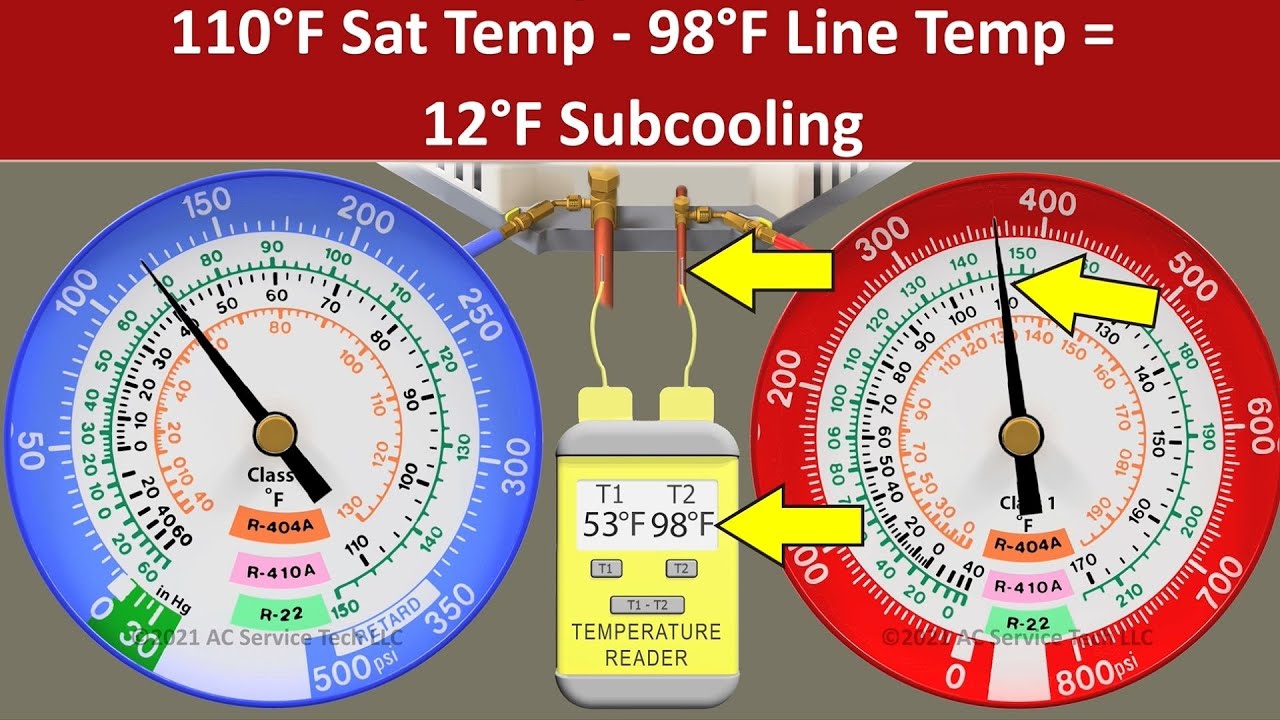
Too low superheat (below 2°f) = risk of flooding the compressor, too high superheat (above 15°f) = risk of overheating the compressor. Web how to measure and calculate superheat and subcooling. You will find the chart that summarizes all total superheats further on. Always refer to the manufacturer's specifications for accurate measurements. Subtract the liquid line temperature from the saturation temperature.
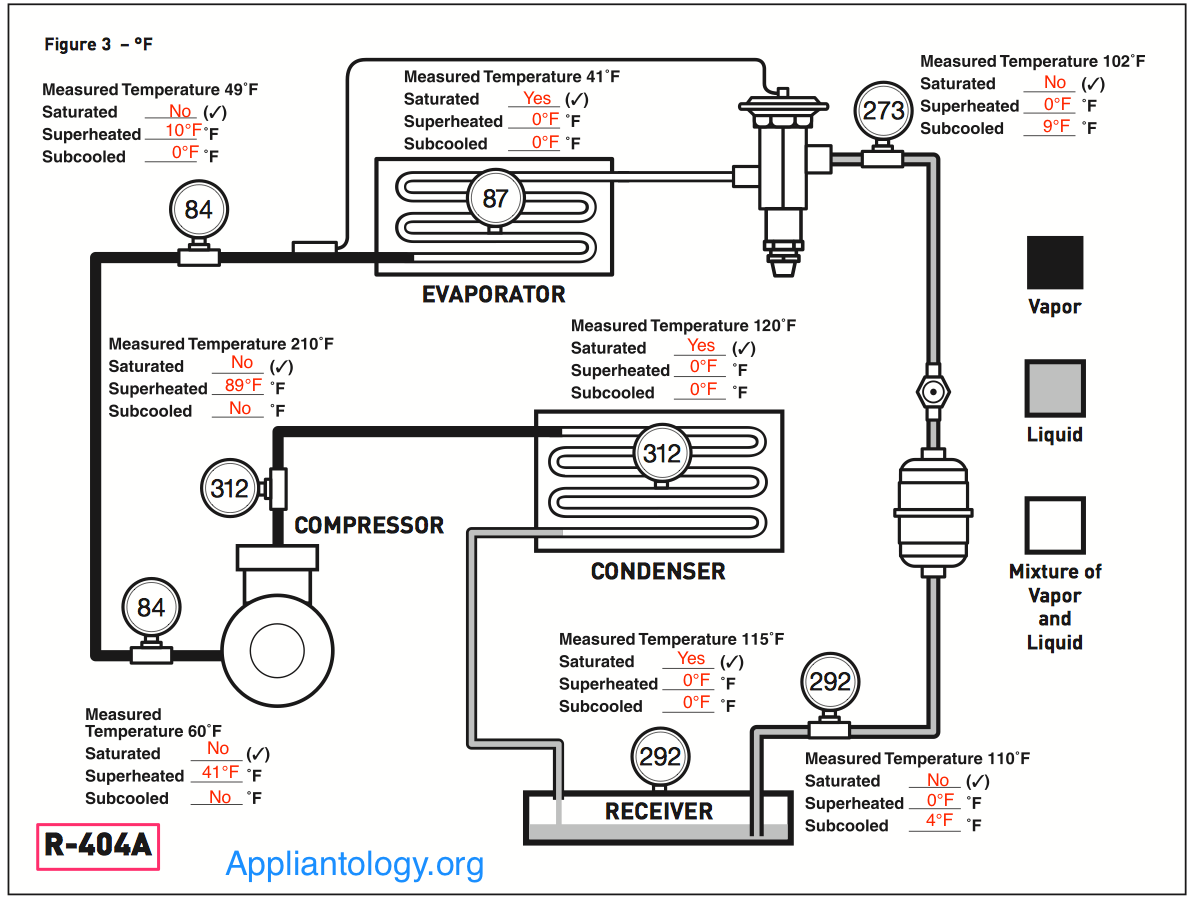
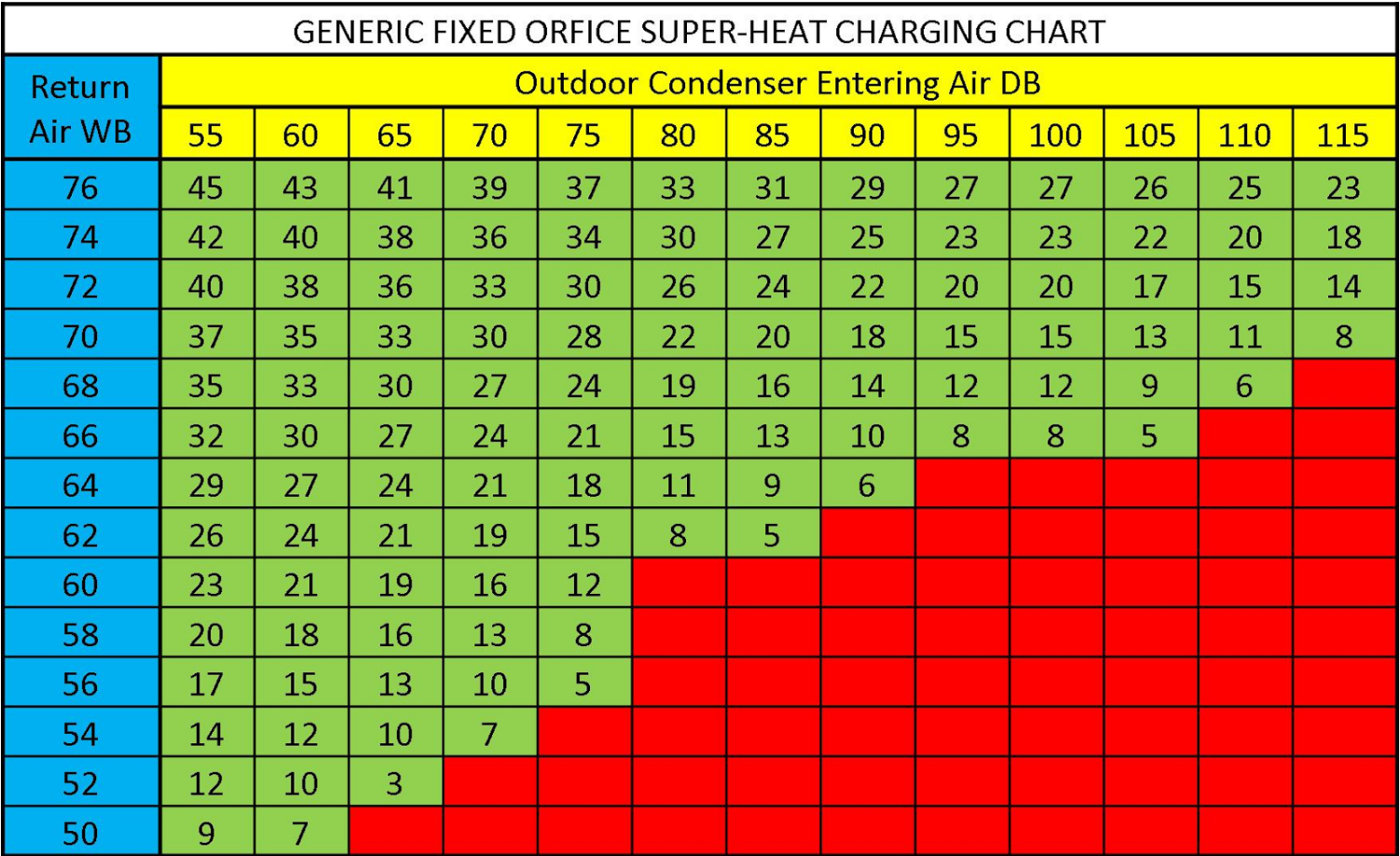
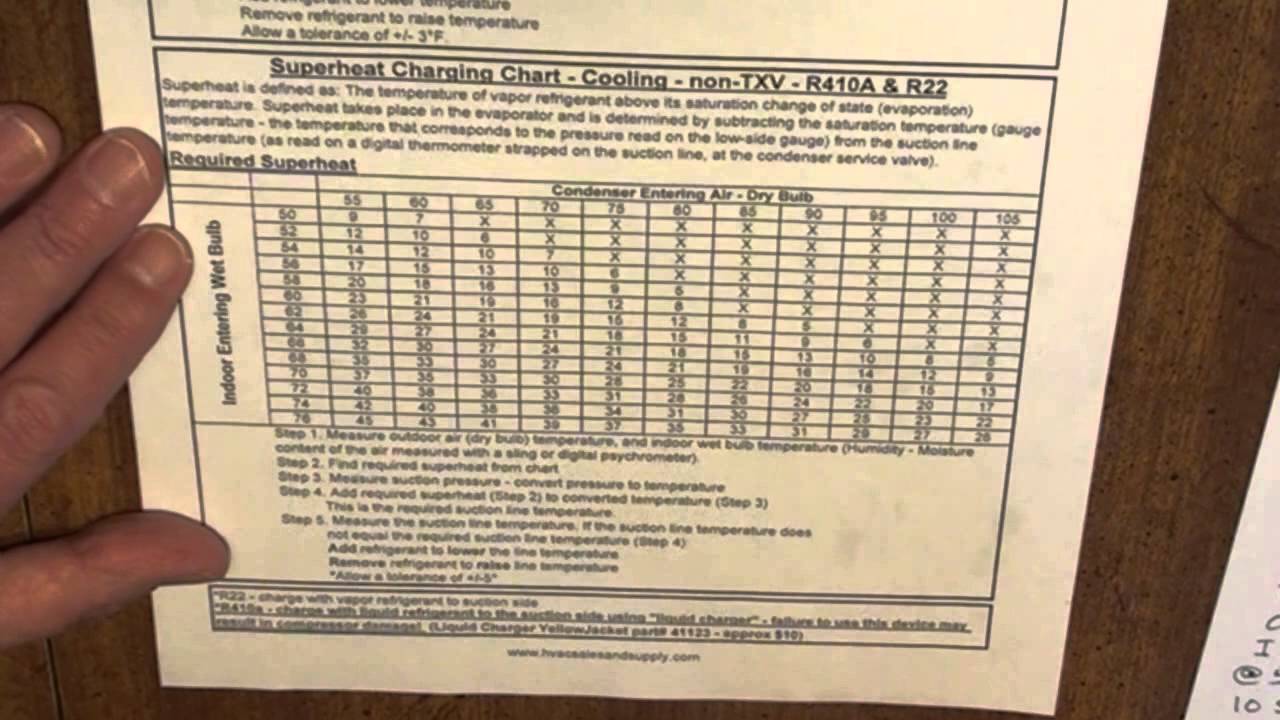
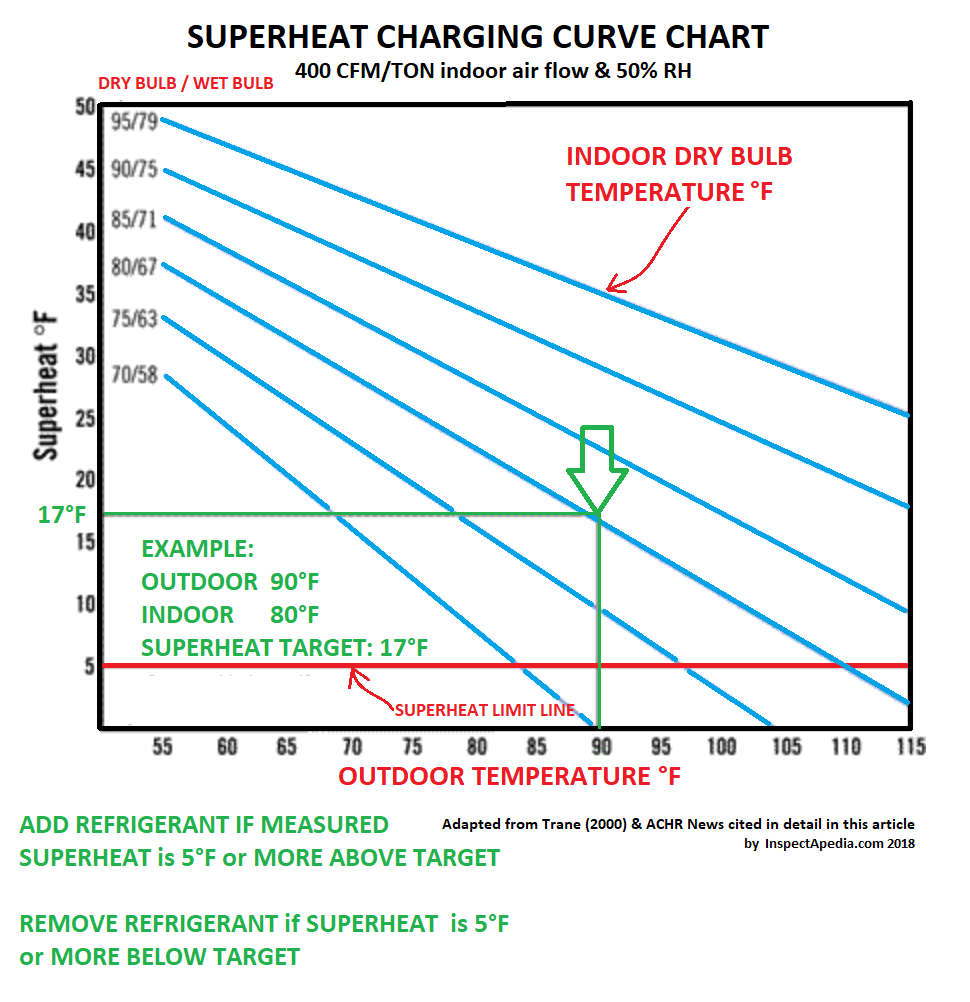
Subtract the saturation temperature from the vapor line temperature. We are usually looking for 7°f to 15°f superheat. Too low superheat (below 2°f) = risk of flooding the compressor, too high superheat (above 15°f) = risk of overheating the compressor. Web once you determine the indoor wet bulb and outdoor dry bulb temperatures, check the manufacturer’s charging chart to determine the proper suction superheat. Just use the button labeled (p/t).
Just use the button labeled (p/t). You will find the chart that summarizes all total superheats further on. Always refer to the manufacturer's specifications for accurate measurements. Subtract the liquid line temperature from the saturation temperature. A system with a fixed metering device must be charged by superheat. We are usually looking for 7°f to 15°f superheat. Web the superheat chart includes target ac superheat for 55°f to 128°f outdoor temperature (db temperature) and for 50°f to 76°f indoor evaporator temperature (wb temperature). Use the refrigerant drop down for access to over 100 refrigerants. Web how to measure and calculate superheat and subcooling. Measuring is a bit hard (pressures and p/t charts), but the superheat calculation is quite easy. Our pressure temperature chart for the selected refrigerant is available for quick access; What are superheat and subcooling even used for? Web once you determine the indoor wet bulb and outdoor dry bulb temperatures, check the manufacturer’s charging chart to determine the proper suction superheat. Too low superheat (below 2°f) = risk of flooding the compressor, too high superheat (above 15°f) = risk of overheating the compressor. Subtract the saturation temperature from the vapor line temperature.
Measuring Is A Bit Hard (Pressures And P/T Charts), But The Superheat Calculation Is Quite Easy.
Web the superheat chart includes target ac superheat for 55°f to 128°f outdoor temperature (db temperature) and for 50°f to 76°f indoor evaporator temperature (wb temperature). Use the refrigerant drop down for access to over 100 refrigerants. We are usually looking for 7°f to 15°f superheat. Subtract the liquid line temperature from the saturation temperature.
You Will Find The Chart That Summarizes All Total Superheats Further On.
Web this free online tool allows hvac professionals to quickly calculate superheat and subcooling measurements for both r22 & r410a refrigerants. Just use the button labeled (p/t). Web once you determine the indoor wet bulb and outdoor dry bulb temperatures, check the manufacturer’s charging chart to determine the proper suction superheat. Web how to measure and calculate superheat and subcooling.
What Are Superheat And Subcooling Even Used For?
A system with a fixed metering device must be charged by superheat. Subtract the saturation temperature from the vapor line temperature. Always refer to the manufacturer's specifications for accurate measurements. Web hvac app to calculate superheat.
Our Pressure Temperature Chart For The Selected Refrigerant Is Available For Quick Access;
Web superheat determines by how many degrees of temperature refrigerant vapor increases in the system. Too low superheat (below 2°f) = risk of flooding the compressor, too high superheat (above 15°f) = risk of overheating the compressor.